论文总字数:24214字
目 录
1 引言 3
1.1立题背景和意义 3
1.2水体富营养化 3
1.2.1水体富营养化的危害及成因 3
1.2.2水体富营养化发生条件及控制措施 4
1.3富营养化水体生物修复的理论基础 6
1.3.1沉水植物在水体修复中的作用 6
1.3.2底栖动物在水体生物修复中的作用 7
1.3.3底质的作用 8
1.4研究内容和目的 8
2 实验设计 8
2.1实验思路与实验预期 8
2.2实验材料 9
2.3实验装置 9
2.4 实验步骤 10
2.5数据测定与处理 10
2.5.1苦草各指标 10
2.5.2水体理化性质测定 11
2.5.3数据处理 12
3 实验结果 13
3.1水体理化指标 13
3.1.1总氮(TN) 、总磷(TP)变化 13
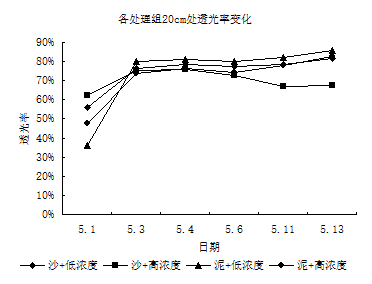
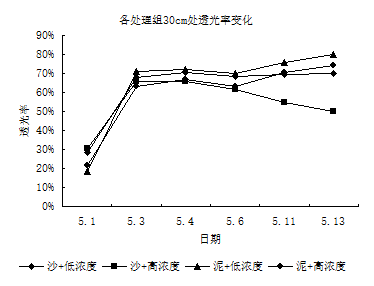
3.1.2透光率变化 14
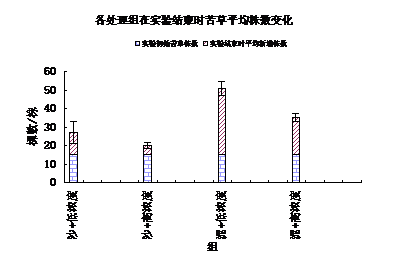
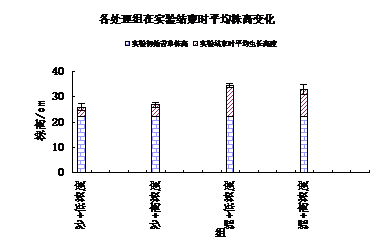
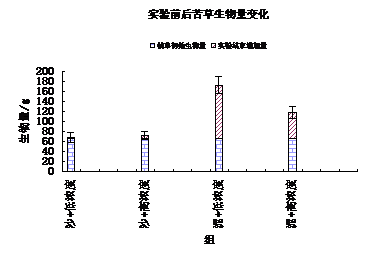
3.2苦草变化 14
4 讨论 16
5 结论 17
参考文献 18
致谢 20
不同底质条件下水体富营养化与“河蚌-苦草”系统的相互影响
王明飞
,China
Abstract:Eutrophication will promote algae blooms, resulting in aquatic plants especially submerged macrophytes in decline or even disappear and ultimately destroy the ecological balance of the river basin,eutrophication has become a worldwide problem. Submerged plants are the primary producers of lake ecosystem and the foundation of biological community formed in the lake, many scholars suggest that the submerged plant is the key factor to keep the state of clear lake ecosystem. Therefore, the maintenance and restoration of lakes in the submerged plant in the process of treatment of eutrophic water has attracted wide attention of scholars. However, research concerned with the mechanism of the effect that eutrophication makes on submerged plants and the effects of submerged plants on the process of water eutrophication is not common. This paper mainly from two aspects of that the effects of different load of eutrophication process and the difference of stratum on Vallisneria spirals to explore the interaction and mechanisms between submerged plants and eutrophication process. Draw the following conclusions:(1)The nutrient content of sediment is richer than sand, and the sediment has a certain contribution to the content of nitrogen and phosphorus in water;with the persistent low concentration nitrogen and phosphorus load (130μgN·L-1d-1,5 μgP ·L-1d-1),the total nitrogen removal of Mussel—Vallisneria spirals system with sand or sediment is significant Removal rate is50.60%、50.49% separately. (2)The response of Vallisneria spirals growth to the process different N and P load (high load 390μg N·L-1d-1、15μg P·L-1d-1,low load 130μg N·L-1d-1,5 μg P ·L-1d-1)eutrophication is different, the average ramets and biomass of low nutrient load treatment increased significantly more than high concentration nutrient load treatments suggests that high nutrient loading has an inhibitory effect on the growth of Vallisneria spirals; With continuous nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient load ,the promoting effect of sediment on the growth of Vallisneria spiralis is better than that of river sand, In other words, Vallisneria spiralis growth in the sediment have a strong tolerance of sustained external nutrient load than that of Vallisneria spiralis growth in river sand. Therefore in the recovery in eutrophic water Vallisneria spiralis is not recommended as a phytoremediation. (3) The mussel makes an important influence on the growth of Vallisneria spiralis and on the continuity and stability of the system, Mussel can reduce the total phosphorus content in water, improve water transparency in a short period of time, improve the light quantity Vallisneria spiralis that received, and make a certain contribution to the average number of ramets and biomass of Vallisneria spiralis。
Key Words:Eutrophication; bioremediation; submerged macrophytes; sediment
1引言
1.1立题背景和意义
随着经济社会的持续发展、城市化的快速推进人们的生产方式、生活方式发生了深刻变化,生活用水、农业用水、工业用水不断增加,淡水资源日益紧张。水是人类赖以生存的根本,而中国657个城市中,有300多个属于联合国人居署评价标准的“严重缺水”和“缺水”城市。水污染已由支流向主干蔓延,由城市向农村扩展,由地表水向地下水深入,由湖泊陆地向海域发展,保护淡水保护水源是事关国计民生的迫切问题。生活污水、农业污水排放量不断增加,随之带来的环境污染问题也越来越严重。水体富营养化已成为我国突出的环境问题之一,《2012年中国环境公报》[1]指出在监测的60个湖泊(水库)中,富营养化状态的湖泊(水库)占25%其中轻度富营养状态和中度富营养化状态的湖泊(水库)占比为18.3%和6.7%,形势依然严峻。
太湖是我国第三大湖泊位于江浙沪交界处,该区域内人口稠密经济发达,也是水污染的重灾区,上世纪九十年代太湖蓝藻水华暴发,致使46家无锡企业被迫停产,造成直接经济损失高达一亿多元[2];2007年太湖蓝藻事件,给渔业、旅游业带来巨大损失。无锡市自来水水质恶化,由此引发了一场淡水危机,造成了严重的环境和社会问题。水污染问题不但直接降低了人们生活环境的舒适度,而且进一步制约了经济社会的持续健康发展,治理污染已经成为我国贯彻科学发展亟待解决的问题。
1.2水体富营养化
1.2.1水体富营养化的危害及成因
由于自然或人为原因使自然水体中供给微生物生长发育所需的氮、磷等营养物质含量超过正常值,导致水中藻类等微生物大量繁殖并因此造成水中缺氧,鱼类死亡;同时藻类遮光,抑制沉水植物生长甚至使水体从高等植物为主的澄清状态转变为以浮游植物为主的浑浊状态[3],水质恶化并发出恶臭,最终破坏流域生态平衡的现象[4]。通常淡水中发生的富营养化被称为水华,海水中是赤潮。随着富营养化发展造成的水生植物衰退甚至消失是全球范围内的普遍现象,随之而来的藻华灾害,流域生物多样性减少,溶氧减少水质下降危害渔业生产和人体健康破坏流域生态平衡。通过比较胡小贞[5]与较早前黎尚豪[6]做的关于云南洱海的调查可以发现富营养化导致洱海沉水植物在分布、群落结构、优势种和生物量上都发生了显著变化:(1)物种多样性下降,沉水植物由先前的19种减少到调查时的13种。(2)优势种发生变化。上世纪八十年代的第一优势种黑藻分布范围和生物量骤降,成为第四优势种,取而代之的是微齿眼子菜。(3)湖内物种多样性降低,群落结构简单化,生态系统多样性下降。多为一种或少数几种沉水植物组成的单优、共优群落。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:24214字
相关图片展示: