论文总字数:28507字
目 录
1引言 3
1.1 研究意义 3
1.1.1 磁层的定义 3
1.1.2 磁层研究的重要性 3
1.2 近代磁层研究 3
1.3 磁层建模的基本理论 5
1.3.1 二维磁层模型 5
1.3.2 三维磁层模型 5
2 Tsyganenko模型简介 6
2.1 N.A.Tsyganenko简介 6
2.2 Tsyganenko模型 6
3 典型的Tsyganenko模型 7
3.1 T89模型 7
3.2 T96模型 12
3.3 T01模型 16
3.4 T05模型 19
3.5 T07模型 21
3.6 T15模型 22
4 Tsyganenko模型比较分析 25
5 总结与展望 27
参考文献 27
致谢 31
地球磁层的Tsyganenko模型
郭思瑶
,China
Abstract:By understanding of the development history of modern magnetosphere researches and some related magnetosphere models, combined with the basic theory of the magnetosphere modeling, We focused on the analysis of the magnetosphere model of the most representative model --Tsyganenko model (T model). In order to understand the development of the T models, we compared the advantages and disadvantages among different generations of T model. This paper also describes the characteristics of the latest generation of T model -- T15 model, and finally forecasts the developing direction of the magnetosphere modeling. By summarizing it, it is believed that the early model T89 that based on the measured data of the spacecraft can describe the main characteristics of the magnetic field in the calm period, but it can not describe the dynamic changes, especially during the period of disturbance. T96 model is relatively improved, and consider the complex processes of magnetospheric layer. The expressions of the ring current and the magnetotail current are more reasonable, moreover, T96 also considers the relationship between the magnetic field and the interplanetary parameters, the dynamic changes of the during geomagnetic storms can also be reflected. Because some faults still exist, the coming models T01, T05, T07 model adopted more satellite data, such as the MP-8, GOES-8, GOES-9, GOES-10, GOES-12 and synchronous satellite data, the solar wind and interplanetary parameters were considered. These models also selected the cluster satellite data and the dipole field data. The corresponding parameterizations were improved and then simulate different geomagnetic activity is available. In order to study the complex problems that lie in various regions of magnetosphere, such as the calculation of the magnetosphere in every point of the magnetic field vector and IGRF that expressed the main magnetic field, to track lines under the different geomagnetic activities and to draw the magnetosphere shape to calculate the dynamics of the magnetotail plasma sheet and substorm current wedge, to calculate ring current and the magnetic field contribution. But the newest T model still has shortcomings, such as the dynamic change of the magnetic field can’t be described accurately. In the future, we need to focus more on the description of dynamic events.
Key words:Tsyganenko model; Satellite data; parametric method; magnetosphere; magnetic field
1 引言
1.1 研究意义
1.1.1 磁层的定义
磁层是地表上空1000KM处到大气顶界之间的稀薄电离气体层,该层内电子和离子的运动受地球磁场支配。位于地球周围、被太阳风包围并受地磁场控制的等离子体区域,即为磁层[1]。磁层的概念是由Chapman[1]于20世纪30年代首先提出。20世纪60年代,人造地球卫星对地球高带电粒子区域的探测,证实了地球磁层的存在。磁层由磁层顶、等离子体幔、磁尾、中性片、等离子体层与离子体片等组成,在磁层顶外还存在磁鞘和弓激波。
1.1.2 磁层研究的重要性
地磁场是地球的一道屏障,可以防止来自太阳的高能宇宙粒子直接到达地面,从而保护了地球上的生命,而地磁场又是在变化的,所以研究地磁场尤为重要。
地磁场的周期不规律变化的原因是太阳风会持续地在磁层边界将质量,动量送往磁层中,正是这种活动引起了地磁场变动。黑子、耀斑、日冕物质抛射等发生在太阳上的运动,会引起激波和太阳风流、亚暴、磁暴等磁层扰动过程,这些空间天气灾害由增强的太阳风能量造成[2]。太阳耀斑(Solar flare)是一种非常强烈的太阳活动,对地球的危害极大。经耀斑释放出来的能量约等于几十万次的火山爆发所释放出来的总能量,也类似于百亿枚重量级氢弹爆炸的能量。它的辐射会在地球周围出现,与大气分子剧烈撞击后,无线电波会因为被它破坏的电离层从而失去反射等一系列功能,如干扰通信设施、造成通讯故障,电视信号、电台信号等会中断传输。
预测及预报耀斑、磁暴等空间天气灾害的产生对于人类的产生和生活来说有着相当重要的意义。空间天气具有全球性和局域性特征,所以一次灾害性空间天气事件通常会导致全球性的破坏[3],如导致通信系统、导航及定位系统、航天器安全、地质勘探、气象研究业务等遭到破坏。
若想较好地预测空间天气灾害,相关的空间天气模型是一个常用的工具,利用其可研究处于动态的磁层的变化规律,从而较好地预测、预报空间天气灾害,从而减少相关损失。
1.2 近代磁层研究
由于磁层具有重要的理论意义和应用价值,所以人们对其做了很多研究。Chapmam和Ferraro[4]最初在上世界30年代初期,使用具有导电功能的圆柱面和平板来模仿逐渐扩张的日冕的锋面前段,许多后来的研究者也用过类似的方法来进行模拟,这种模拟可以计算出当时磁场的分散范围和畸形变异,这就是向外扩张的日冕流间歇冲撞磁场的假说,该模型即早期的磁层模型。模型还可给出磁场周围的感应电流分布图。1959年Van Allen[2]发现了一种带电粒子在地磁场的牵引下,在封锁的区间运动。这种带电粒子在地球辐射区域中的运动由Van Allen基于Explore-3卫星数据观测到。后来Gold[5]首先用“电离层上方,磁场对高速运转的带电粒子和气体进行主要操纵的区间”这层定义,来表示磁层。
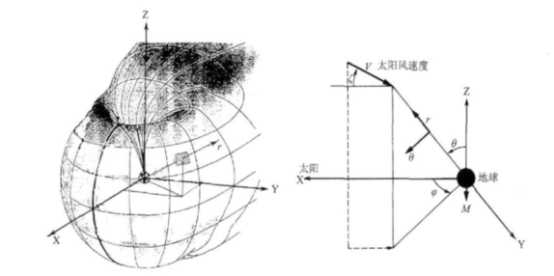
早期使用卫星探测只是勾勒出了磁层的大致轮廓,并没有很细致的描述磁层的具体模型。同期,太阳风和磁层相互作用的纯粹理论研究也在不断发展。Dungy在1961年[6]提出了磁重联模型(开模型)和Axford-Hines[7]提出的似粘滞模型(闭模型)[2],都是重点研究太阳风和磁层间的互相作用。磁层内部大尺度的等离子体的流动图形在结构上和它所产生的电场的图形十分类似,这是都是由以上两种模型所估算得到。此后的一些卫星观测数据证明了一些标志着太阳风输进磁层内的能量,如跨极盖区电位差、磁层对流强度、磁暴和亚暴强度、场向电流[2]等等,都和行星际磁场(IMF)的方向有关,尤其和行星际磁场的南向分量有着特殊而深厚的联系。所有的这些东西都与Dungy的开模型联系更为紧密,更倾向于开模型。图1是基于HEOS 1、2以及IM P3卫星数据的磁层磁场分布图。
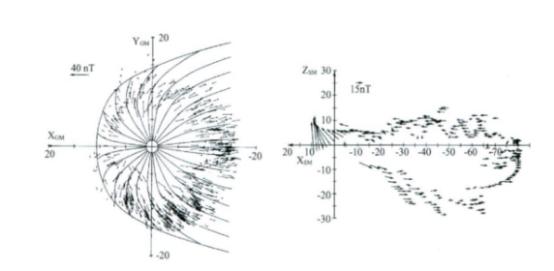
图1 卫星观测到的磁层磁场[2]
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:28507字
相关图片展示: