论文总字数:17898字
目 录
1引言 5
2研究区概况 5
3研究方法 7
3.1降水距平百分率 7
3.2Mann-Kendall法 7
3.3Morlet小波分析 8
4降水变化的时间分布特征 9
4.1降水距平百分率分析 9
4.2季节变化特征分析 11
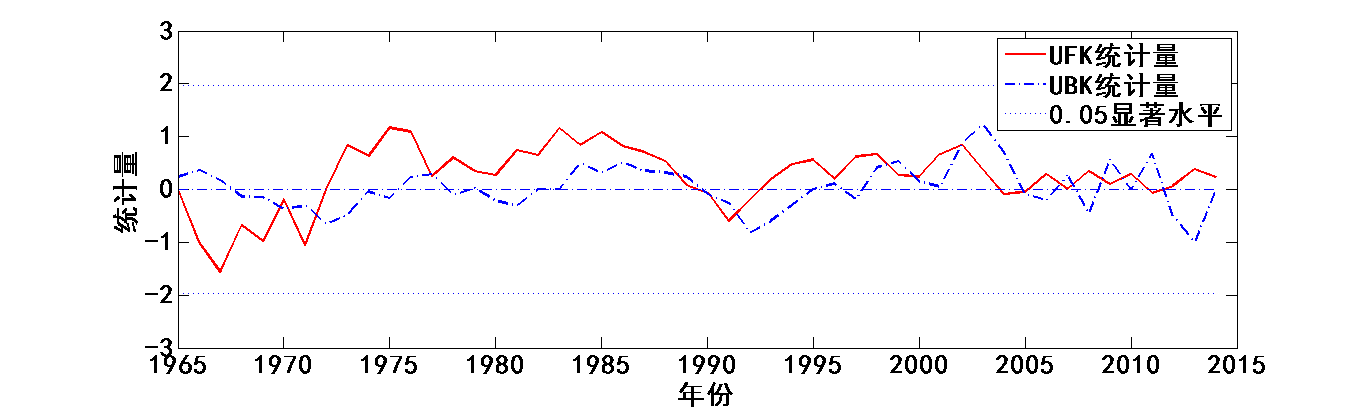
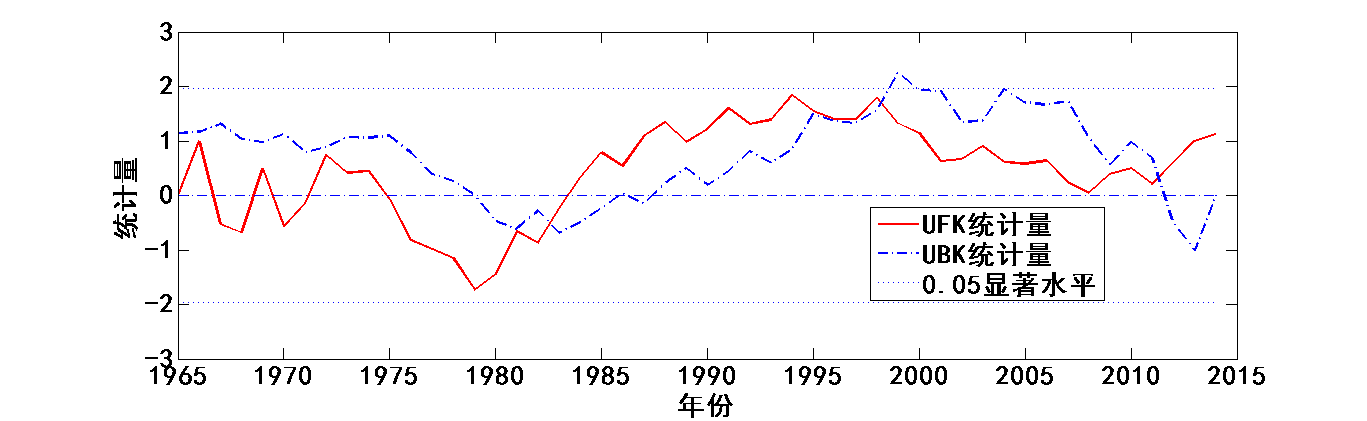
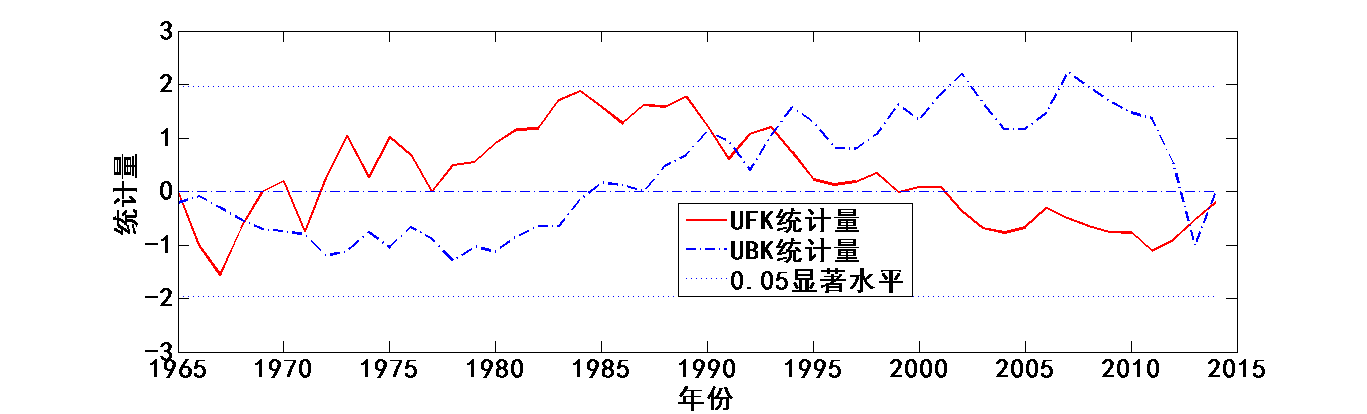
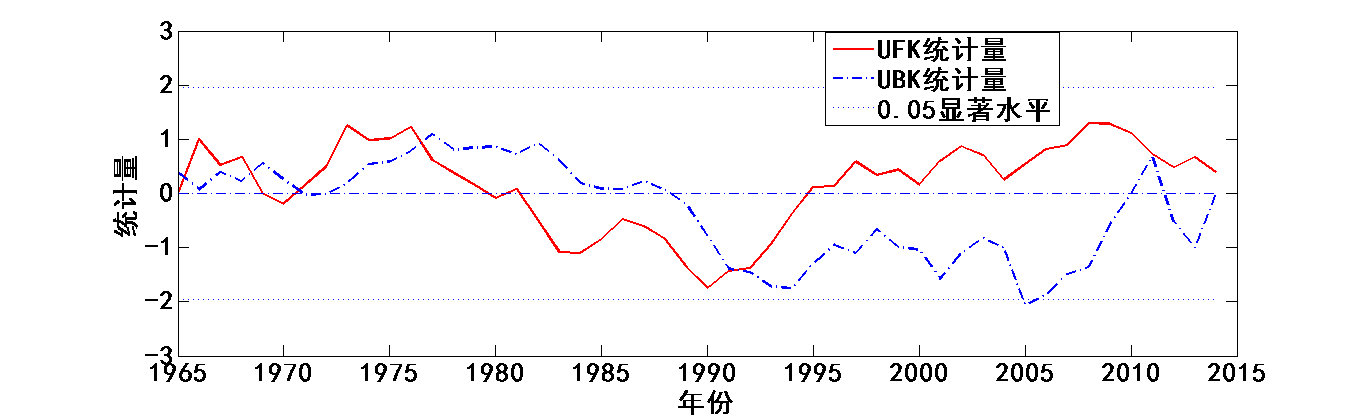
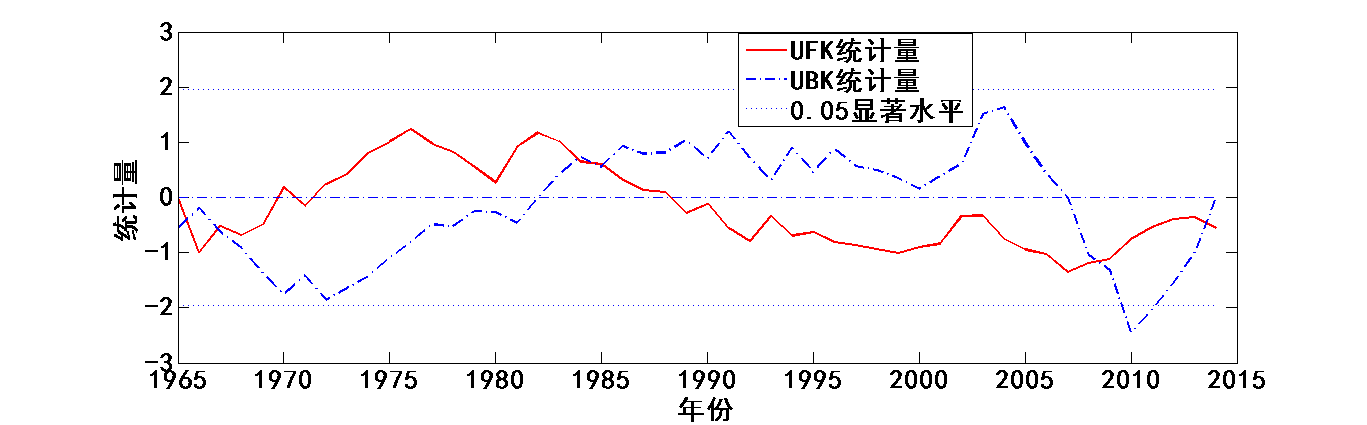
4.3降水趋势变化及突变时间分析 13
4.4年降水序列周期分析 18
5降水的空间分布特征 22
6结论 24
7讨论 25
参考文献 25
致谢 28
1965-2014年我国南北代表区域降水量变化特征比较研究
---以广东和黑龙江为例
贾世杰
,China
Abstract: Meteorological data (daily rainfall) from 1965 to 2014 at 52 meteorological stations of Guangdong and Heilongjiang province were used in this study. With the methods of precipitation anomaly percentage, Mann-Kendall method, wavelet analysis to analyze the change characteristics of precipitation in the two selected provinces. The results showed that: ① the precipitation on the time series of Guangdong province increases slightly, no obvious mutation, there are 18 of interannual oscillation around a cycle and around 11.5 a interannual oscillation period; Seasonal rainfall, summer precipitation is significantly more than any other each season, each season precipitation were not obvious mutation; Diminishing rainfall distribution is roughly from southeast to northwest.② precipitation on the time series in Heilongjiang province is on the rise, there is no obvious mutation, there are about 17.5 the interannual oscillation period and about 11 a interannual oscillation period; Summer precipitation in the seasonal rainfall, significantly more than the other seasons, winter precipitation in 1997 significant mutations, precipitation rate increased significantly; Precipitation rainfall distribution in central area is larger, less rainfall in the west.③ North-south representative area precipitation variation characteristics comparison: total precipitation for the south, the north less rainfall, annual average difference at around 1200 mm; North and south on behalf of area rainfall intensity suffer from seasonal changes and the south is more obvious than the north; On the time series, the north-south rainfall were not obvious mutation occurs, all were obvious cycle and cycle; On the spatial distribution, on behalf of the south area, precipitation differences between the north is not obvious difference between the representative area.
Key words: Precipitation change; The precipitation anomaly percentage; Wavelet analysis; Mann-Kendall method;
1引言
气候变化与人类的生产和生活密切相关,其主要方面体现在全球气候正在发生重大变化。
在全球变暖的总趋势下,全球降水模式发生重大变化,格局进行了调整,高纬度地区降水普遍增加,中低纬度地区降水在许多地方减少。在全球气候发生重大变化,全球变暖的大趋势下,我国近年来的降水量在不同地区也表现出明显的变化。地区降水是重要的环境变量,区域降水对区域气候变化有很大的影响是用来研究气候变化最敏感的和最直接的影响因素。因此,对区域降水及其变化趋势的研究是对全球和区域气候变化研究的基础。
张翀等以线性趋势分析、小波分析以及Mann-Kendall突变检验法为基础,利用1962年-2000年中国西北地区46个气象站点降水数据序列,对中国西北部地区降水变化的时空特征进行了分析[1]。任永健等利用1961-2010年华中区域通过均一化检验的233个站点作为研究对象,系统分析了近50年来华中地区区域降水的变化特征[2]。任利利等采用线性回归分析、Mann-Kendall突变检验、空间插值及小波分析等方法,利用MATLAB等软件分析了汉江上游地区降水时空变化特征,并且对区域内4个典型分布的地区间的差异进行了对比[3]。
气候变化的研究是世界性课题,很多学者采用了不同的研究方法。可见,采用小波分析法和Mann-Kendall法对气候要素进行分析应用也很广泛,具有一定的可信度。本文即采用了的降水距平百分率分析、小波分析、Mann-Kendall突变检验法对广东省和黑龙江省1965-2014年共50年的降水量时空特征进行分析,研究结果将对研究全球气候变化背景下中国不同气候区气象要素的变化特点有重要意义,并为中国的生产规划,对气候变化的适应能力,实现社会、环境和经济的可持续发展提供参考,了解区域降水量的变化趋势对采取相应措施保障生态系统有一定的指导作用,对比南北代表区降水量在时间序列的变化趋势以及空间分布为人类生产活动提供参考性意见[4-6]。
2研究区概况
广东省地处中国大陆最南部。东部紧临福建,西部连接广西,南部比邻南海,北部与江西、湖南接壤,珠江口东西两侧分别与香港、澳门特别行政区交壤,西南部雷州半岛隔琼州海峡与海南省相望。全境位于北纬20°09ˊ~25°31ˊ和东经109°45ˊ~117°20ˊ之间。本文选取了广东省境内分布均匀的25个气象站点,获取了每个站点1965年-2014年每天的降水量数据。
黑龙江省位于中国最北部,是我国最东、纬度最高、经度最东的省份。黑龙江省东起135°05′,西至 121°11′,南起43°25′,北至53°33′,南北跨10个纬度,2个热量带;东西跨14个经度,3个湿润区。本文选取了黑龙江省境内分布均匀的27个气象站点,获取了每个站点1965年-2014年每天的降水量数据。
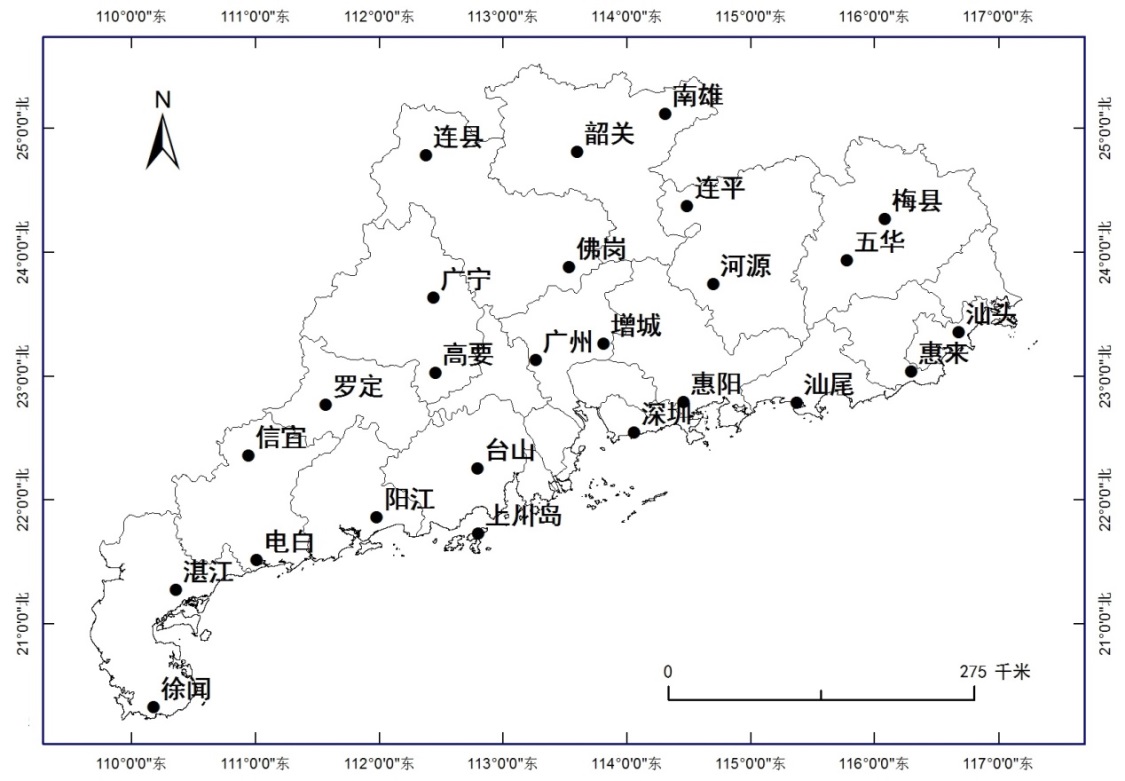
图 1 广东省站点分布图
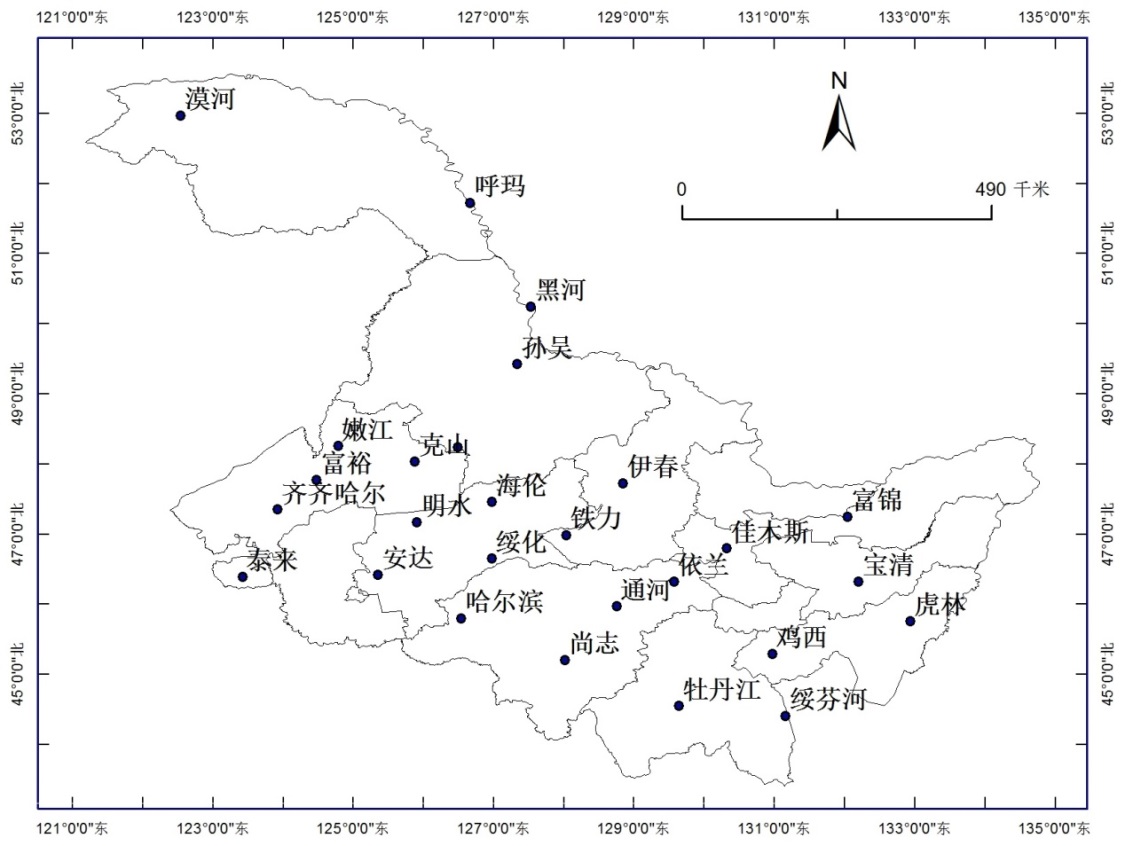
图 2 黑龙江省站点分布图
3研究方法
3.1降水距平百分率
降水距平百分率反映了一个地区一段时间内,水文要素值偏离多年同期平均降水量的程度[7],反映出是否出现降水异常以及异常程度。计算公式为:
式中:表示降水距平百分率(%);P表示某时段内降水量(mm);表示多年平均降水量(mm)[8-10]。
3.2Mann-Kendall法
Mann-Kendall法是一种用于检测突变的新方法,主要用于时间序列趋势分析。现在已被广泛使用于气象要素的分析,被气象组织推荐。该方法计算简便,明确显示突变的开始时间,十分有利于分析降水要素时间序列的趋势变化[11]。
在Mann-Kendall法检验中,原假设是n个独立变量同分布的时间序列样本数据(,…,);备择假设用于双边检验,对于所有的k,j≤n,并且k≠j,和的分布是不相同的,统计变量S的计算公式如下[12]:
其中,
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:17898字
相关图片展示: