论文总字数:20370字
目 录
1、引言 ……………………………………………………………………1
2、数据与方法 …………………………………………………………3
2.1气象要素场………………………………………………………………………………3
2.2地表覆被类型数据………………………………………………………………………5
2.3蒸散和产水量……………………………………………………………………………6
3、鄱阳湖流域蒸散和产水量的时空变化特征………………………7
3.1鄱阳湖流域蒸散和产水量的空间分布特征……………………………………………7
3.2鄱阳湖流域蒸散和产水量的变化特征………………………………………………… 8
4、气象因子和地表覆被类型对蒸散和产水量的影响………………8
4.1 气象因子对蒸散和产水量的影响……………………………………………………8
4.2地表覆被类型对蒸散和产水量的影响……………………………………………14
5、结论与讨论……………………………………………………………18
参考文献…………………………………………………………………19
致谢…………………………………………………………………21
鄱阳湖流域蒸散和产水量时空变化研究
曹菁
,China
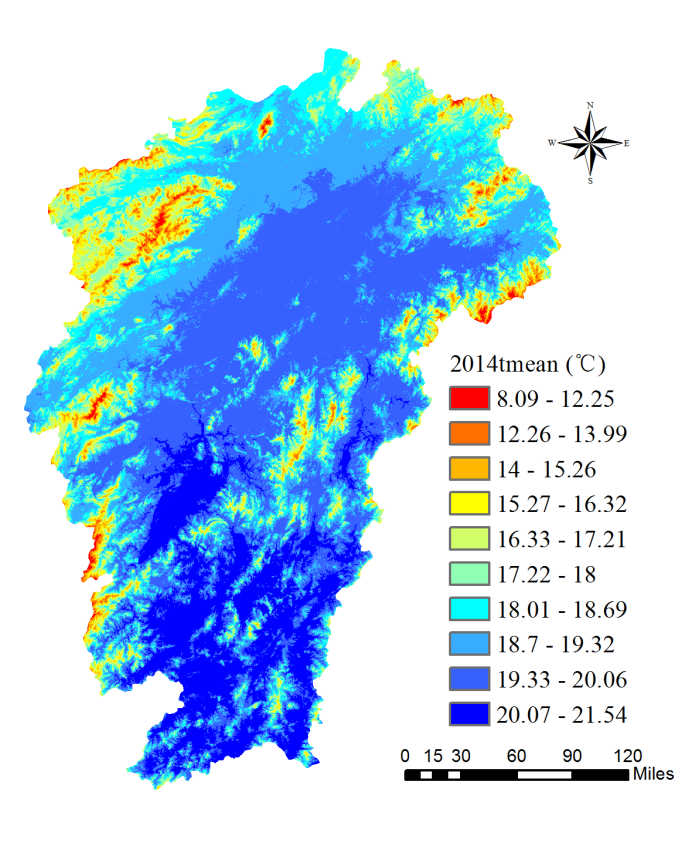
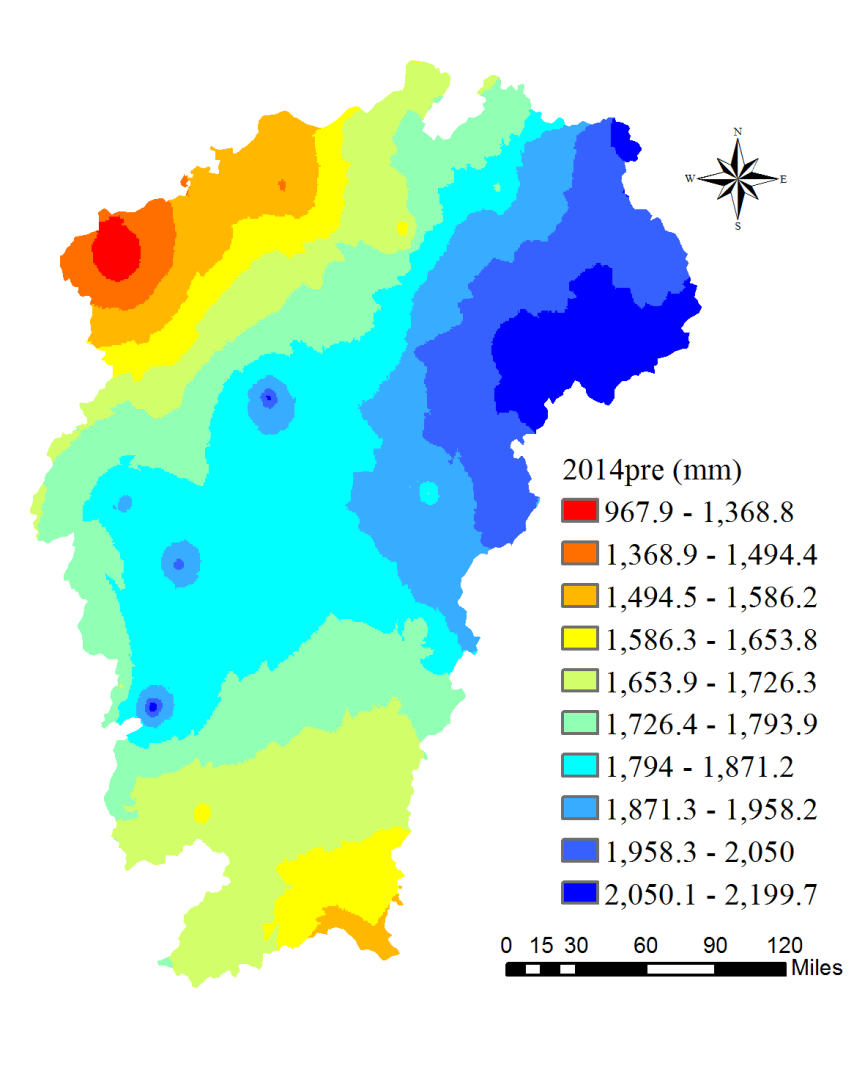
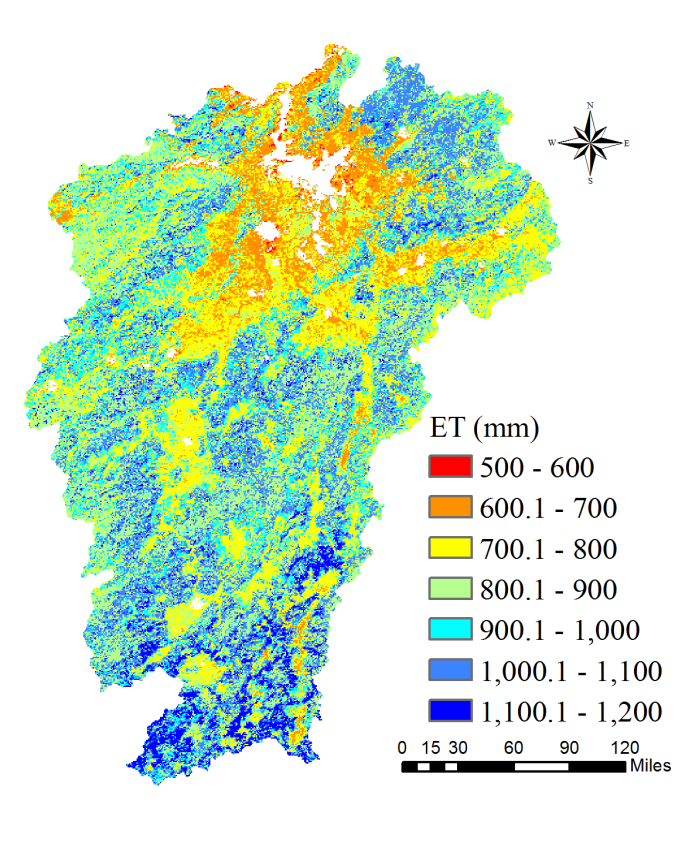
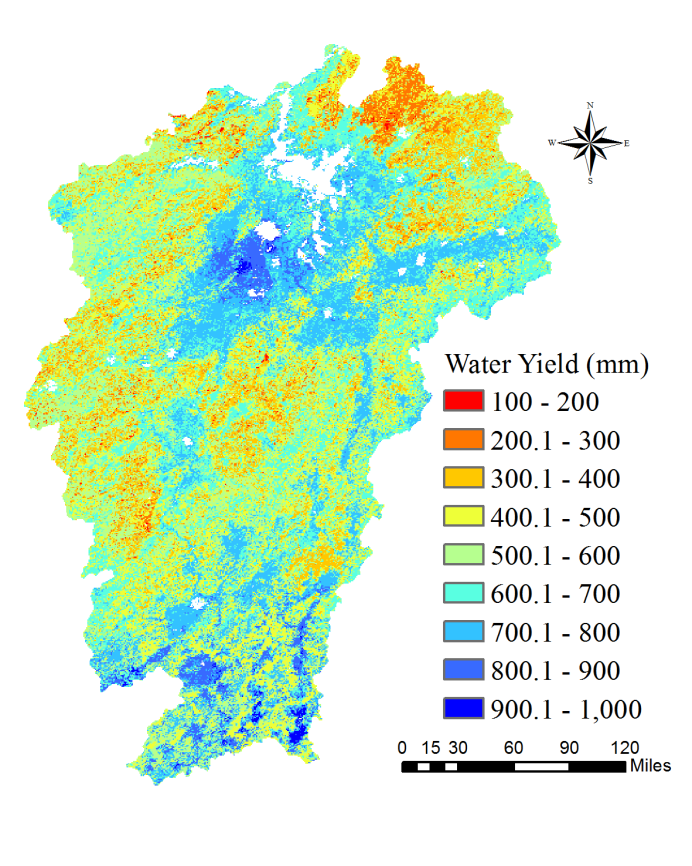
Abstract:ET is an important component of land surface hydrological process, which determines the water and heat transmission in the circulation system. Climate changes and land cover type changes have some deep influences on ET and water yield. Research on the rule of temporal and spatial variations in Poyang Lake Basin can provide scientific references for water resources management in the background of frequent extreme weather events. In this study, the ET and water yield of Poyang Lake Basin under different climatic conditions and land cover types were studied by using remote sensing inversion product and ground observation data. This article focuses on the ET and water yield in the river basin during 2000-2014.The results showed that:(1) The highest value of ET in Poyang Lake Basin during 2000-2014 was concentrated in the southern part, with the lowest value occurring around the lake district. ET is increasing from north to south except the lake area, roughly from 700 to 1000mm. The lowest value of water yield (precipitation - evaporating) is in the northern boundary, and the highest peak is in parts of the south and the lake surrounding area. Water yield in most of the basin is maintained at 500-700mm. (2) Under normal conditions, the average annual precipitation is less, the received solar radiation is more, the temperature is higher, the annual ET is larger, and vice versa. The conclusion of water yield can be drawn in contrast. (3) ET intensity of different land cover types in Poyang Lake basin is roughly like:Urban<Barren lands<Croplands<Grasslands<Forest. ET in the forest area is of high value, mainly in the south of the basin. The actual ET values were lower in the fields around the lake. In the spatial distribution, the surface ET showed the characteristics of low in the middle and high in the surrounding areas. The higher the vegetation coverage, the higher the ET. The change of water yield is contrary to ET.
Key words:Evapotranspiration (ET);water yield;climate change;land use and land cover change;Poyang Lake Basin
- 引言
蒸散(Evapotranspiration,ET)定义为植被和地面向大气输送的水汽总通量。该通量不仅包含地表和植物表面的水分蒸发,还包含植物表面和体内的水分蒸腾[1]。蒸散决定了土壤—植被—大气(SPA)系统中的水分和热量传输,是陆面水文过程中极具重要意义的分量,也是水文水循环与水量平衡研究的核心。产水量的定义为在给定时段内,从单位流域面积上所产生的河川径流量。目前对蒸散和产水量的研究已得到国内外学者的广泛关注,并取得大量进展。
气候变化加速了水文循环过程,气象因子对于蒸散和产水量的影响直接而深远。以往的研究表明,气候变化可能会导致洪水与干旱更加频繁[2]。进一步的升温将深入推动这一趋势。一般而言,气候系统中蒸散的变化可以基本维持在一个相对稳定且平缓的水平,尽管降水往往具有不连续性和突变性。实际的蒸散值存在着空间异质性大的特点,受气象因子如气温、降水、辐射、风速、相对湿度等的影响较大[3],但通过对温度、降水和太阳辐射等的研究,可得出其作用的一般规律。而土地覆被类型及地表水分分布等多种因素的影响,流域尺度下的实际蒸散无法直接测量,甚至难以粗略估算。需借助遥感数据,进行分区统计,进一步得出蒸散和地表覆被的分布与变化规律。
不同的地表覆被具有不同的下垫面物理特性(如地表反射率、辐射的吸收能力、热传导能力和地表粗糙度等),在一定程度上会引起地表的不均匀性。即不同的地表覆被类型所对应的动力和热力性质的差异会造成流经其表面的气流的物理特性产生变化。在这种地气系统的相互作用下,不同地表覆被类型能量重新分配,继而引发地表热通量和蒸散量以及产水量的空间差异[4-5]。所以,准确地把握好鄱阳湖流域不同地表覆被类型下的蒸散量及其空间分布特征,不但可以深入了解并掌握陆面水循环和水平衡过程的规律,同时对于流域水资源的合理管理、利用与评价、旱涝多发地区灾害的特征分析以及旱涝灾害的监测和预警机制等研究具有重要意义。
为了更好地了解大气和地表间的相互作用、在气候变化的条件下改善水资源管理和干旱评估,准确估算蒸散的时空变化显得至关重要[6]。然而,由于景观的异质性和众多的控制因素,包括气候、植物生物物理学、土壤性质、地形等等,蒸散成为了陆地水循环系统中最难以准确估算的组成部分[7]。准确把握不同地表覆盖下的流域的蒸散量及其空间分布特征,研究流域蒸散和产水量的空间分布格局与时间变化规律,探讨主要气象因子(气温、降水、辐射等)对蒸散和产水量变化的影响特征与机制,有助于加强对地表和流域水循环过程的认知,深入了解旱涝灾害的成因,理性分析并开展防治工作。同时,准确估算蒸散和产水量对于流域水资源合理利用与评价、旱涝灾害成因与发展的特征分析以及旱涝灾害的监测与预警等研究提供科学依据,对解决流域生态环境问题和水资源管理利用具有重要意义。
在点面空间尺度下的现场测量中,使用蒸渗仪、波纹比、液流米和涡度协方差技术通常认定为能够可靠地量化蒸散[8]。然而,这种方法却不能够被应用于区域和全球尺度下蒸散的量化。幸运的是,遥感技术能够捕捉大面积时间连续的地面信息,为地面参数反演提供了一个有效的控制蒸散的工具[9]。这些遥感表面参数,如叶面积指数、土地覆盖、聚集指数、反照率、温度和发射率已经成功地用于直接估算蒸散或驱动基于过程的来模型计算蒸散[10]。
近几十年来已经开发了各种模型使用遥感数据来估算蒸散[11],包括表面能量平衡模型(一个源和两个源的模型)[12]、实证统计模型[13]、物理模型(Penman-Monteith公式)[14]和水平衡模型[15] 等。近期,Li et al.(2009)等人以及王和狄金森(2012)已经核验了这种使用遥感数据来计算蒸散的方法[16]。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:20370字
相关图片展示: