论文总字数:17313字
目 录
1引言 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2 国内外研究进展 1
1.3 研究目的及路线 2
2资料与方法 3
2.1 研究区域概况 3
2.1.1地理状况 3
2.1.2 气候特点 3
2.1.3 农业状况 3
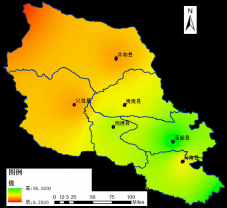
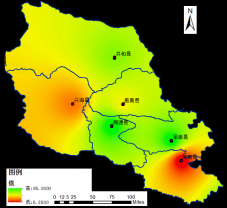
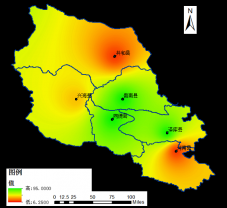
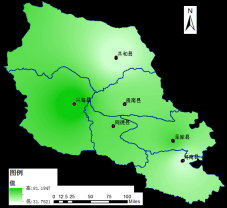
2.1.4 站点分布图 3
2.2 研究方法 4
2.2.1 标准降水指数(SPI)的计算 4
2.2.2无量纲化数据处理---极值法 5
3结果分析 6
3.1 青海东部农业区农业气象干旱危害性评估 6
3.1.1农业气象干旱危害性评估计算 6
3.1.2 研究区农业气象干旱危害性评估分析 7
3.2 青海东部农业区农业气象干旱脆弱性评估 9
3.2.1 农业气象干旱脆弱性评估计算 9
3.2.2 研究区农业气象干旱脆弱性评估分析 10
3.3青海东部农业区农业气象干旱风险性评估 11
3.3.1农业气象干旱风险性评估方法 11
3.3.2 研究区农业气象干旱风险性评估结果 11
3.3.3 青海东部农业区应对农业气象干旱对策 12
4结果与讨论 12
4.1 结论 12
4.2 不足与展望 13
参考文献 13
致谢 15
青海东部农业气象干旱灾害风险性评估
陈雪娇
, China
Abstract: Qinghai Province entrenched in the northwest of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the climate is continental plateau climate. Due to less precipitation in Qinghai, the occurrence of drought, high altitude and low temperature, so the local agricultural development is very limited by natural conditions. Agricultural meteorological drought is the most important meteorological disaster restricting the development of agriculture in Qinghai, so it is very important to carry out risk assessment. The drought risk assessment of agricultural meteorology in this study adopts the "two factor" formation theory. These two factors are the disaster-causing factors and disaster-bearing bodies of the drought system. Firstly, we collected the meteorological data of six typical sites in eastern Qinghai from 1980 to 2009.Then, we calculate the month-scale of the standard water index. To calculate the drought hazard index ,we should according to the SPI index, the drought level of the study area is divided,and statistics of the number of droughty occurrences of different grades. Sencondiy, according to the economic situation, population situation and land use type and disaster resistance ability of the study area, the vulnerability index of economic, population, land use vulnerability and disaster resilience of the study area were calculated respectively, and the vulnerability index of the study area was obtained. After normalizing the non-dimensional treatment of the Drought Hazard Index and the Drought Vulnerability Index, We use ArcGIS's inverse distance interpolation to obtain the distribution of drought hazard and vulnerabilities in the study area. Finally, we use ArcGIS's layer stacking method to evaluate the risk of agrometeorological drought in the study area, and put forward the scientific and arid management suggestions and opinions according to the research results. The results show that the harm of Zeku County is the highest, and the harm of the southern Mongolian Autonomous County is the least. The harm of the central region is higher than that of the north and the south. Xinghai County, the highest vulnerability of agricultural drought, Zeku County second, Guinan County, Tongde County two high vulnerability, Republican, Henan Mongolian Autonomous County, the lowest vulnerability. Zeku County agricultural drought risk the highest, followed by Germany, Henan Mongolian Autonomous County is also a higher risk, Xinghai County, Guinan County lower risk, Republic of the lowest risk. In general, the risk of agricultural drought is significantly different from north to south, the highest in the central region.
Key words: Eastern Qinghai; Agrometeorological Drought; Risk; Assessment
1引言
- 研究背景
干旱是在农业生产季节,长期无降水,使得空气干燥,土壤含水量不足,农业物生长发育受到影响,严重时甚至死亡的一种农业气象灾害[1]。
在全球气候变暖,水资源愈来愈紧缺的大背景下,干旱已经跃居全球危害最大、影响范围最广的自然灾害之一。据测算,每年由于干旱使得世界经济损失约70亿美元,农业部门损失尤为严重。据不完全统计,干旱已经导致死亡人数已达约56万亿人 [1]。在非洲和中亚等地区,由于缺水导致的人员伤亡、战争等,导致这些区域“滴水如金”。
在我国,干旱的危害也是不容小觑的,无论在影响的范围还是发生的频率上,旱灾均 “名列前茅”。我国地处北半球,亚洲东部,位于季风区的地域占绝大部分。随人着全球气温不断上升,水资源愈加紧缺,旱灾影响范围越来越广,造成的不良后果也愈加严重,对经济、农业等各方面危害也更大了[1]。从气象统计资料中可以得出,干旱在所有气象灾害中所占比例突出,且一旦出现,无论是后果还是影响均十分严重 [4]。由于农业气象干旱危害愈加严重,各国对其关注程度也随之增加[1-5]。加上科研水平的提高,风险评估学的发展,国内外学者和有关部门开始将更多地精力放在农业气象干旱的风险性评估和预测上[6]。提高干旱的风险性评估的准确性,对于我国农业发展,以及灾情防御等意义重大。
青海省气候类型是典型的大陆性高原气候,其东部地区是该省粮食的主要生产区域,属于暖凉温半干旱气候区,降水量和降水持续时间等均与农业生产息息相关。尤其是在小麦的生长季,即春季和夏季,是干旱发生次数较多的季节,对农业造成的影响最为严重[5]。从青海省气象灾害普查表统计结果中可以得知,自1984至2006的22年里,共发生123次气象干旱。其中受影响最大的是小麦 [3]。所以青海东部是发生干旱的高风险区域,同时也是政府救灾部门的重点防治地区,因而对该区域进行干旱的风险性评估意义显得重大。而且区域气象灾害的评估对于防灾减灾有极其重要的地位,无论是灾情认识、灾害区划、预测和制定防灾政策、灾损评估、防治措施,还是建立灾害保险制度、制定政府辅助决策等,都要在区域灾情评估的基础上进行[3]。
因此,本文以青海东部六个相关站点为研究区域,对其干旱的风险性进行评估,以期在对研究区农业气象干旱进行较为合理的风险评估后,分析结果,提出较为合理有效的农业气象干旱灾害的风险性评估方法和应对对策,为以后减少干旱带来的危害作出相应指导,避免盲目抗旱带来的不必要的损失的目的。本研究不仅对我国农业干旱风险管理十分重要,而且对我国经济发展,环境保护,第一产业发展也作用巨大[6]。
- 国内外研究进展
灾害风险的形成及评价的研究起源于20世纪80年代初,基于系统学和风险管理学,研究出灾害的成因及其风险有关因素,和两者之间的联系,并用数学表达式表示该联系。根据研究,当前学者们认为,致灾因子,孕灾环境,以及承灾体和三者组成的系统与灾害风险型评估密切相关[7],并根据此,划分为“二因子理论”、“三因子理论”“四因子理论”[8]。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:17313字
相关图片展示: