论文总字数:22658字
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract II
1.绪论 1
1.1研究的意义和背景 1
1.2国内外研究现状 2
1.2.1干旱的分类 3
1.2.2干旱的评价指标 4
1.3研究内容和技术路线 6
2.研究区概况 7
2.1地理位置 7
2.2地形地貌 8
2.3气候条件 8
2.4社会经济概况 8
3.研究数据与方法 9
3.1数据来源 9
3.2降水数据 9
3.3数据处理方法 10
3.3.1降水距平百分率的计算 10
3.3.2干旱等级标准 11
3.3.3干旱频率的计算 11
3,3.4空间插值方法 11
4.结果分析 12
4.1年尺度时空变化特征 12
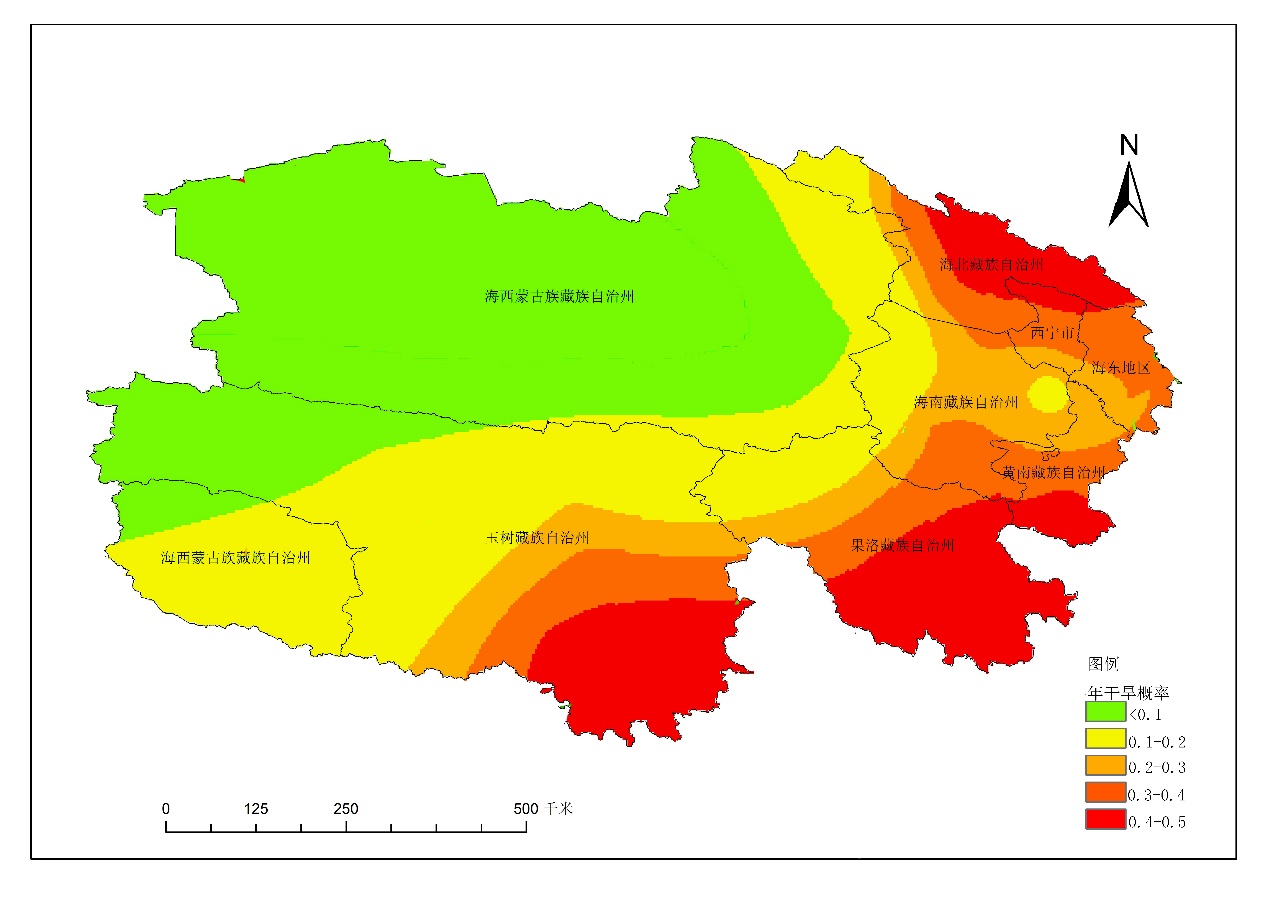
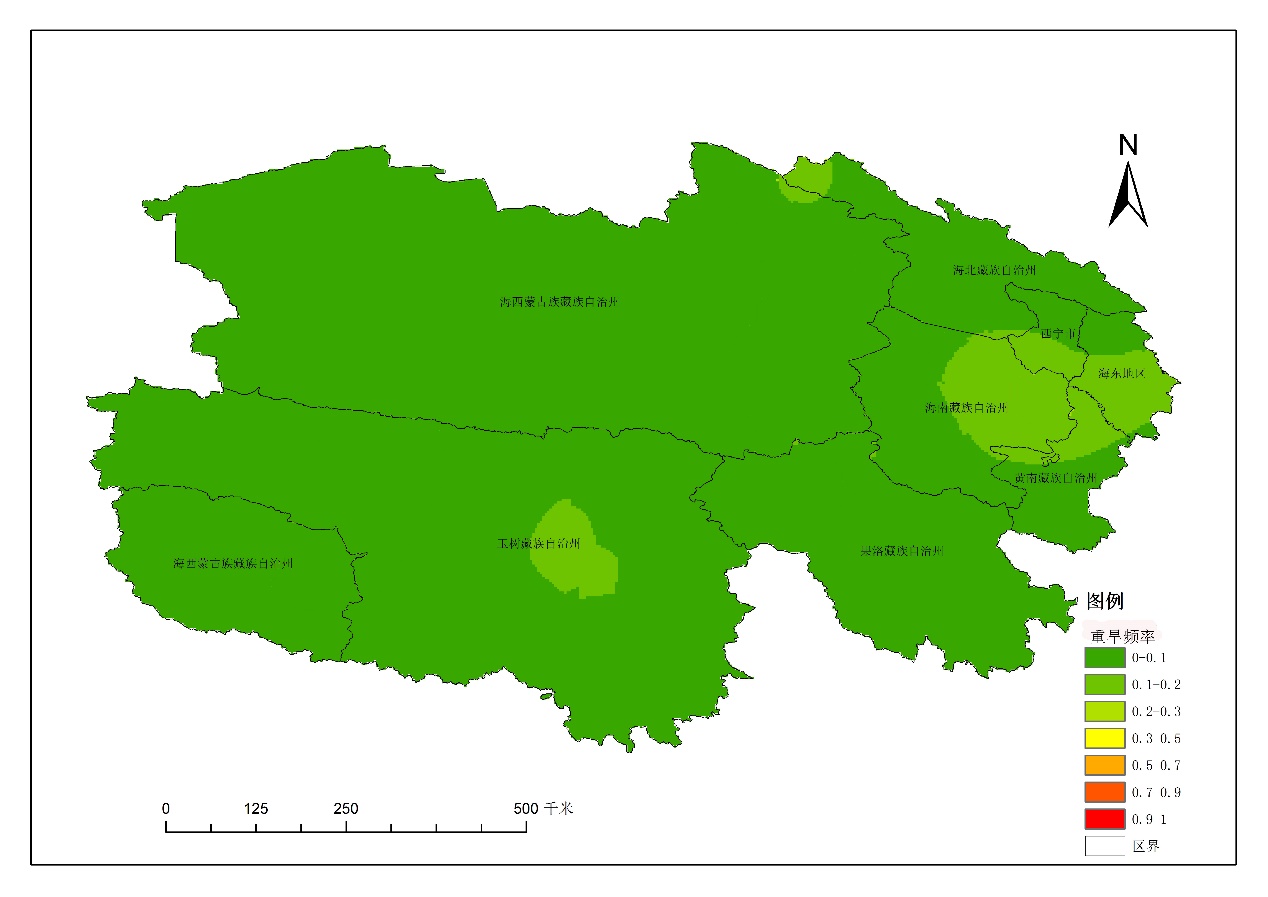
4.1.1年尺度干旱发生频率的空间分布特征 12
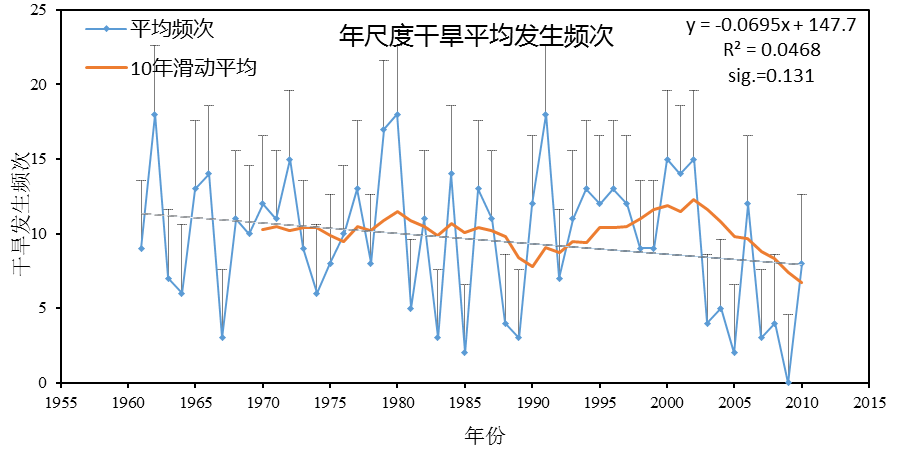
4.1.2年尺度干旱频次时间变化特征 13
4.1.3年尺度干旱强度分布特征 14
4.2季节尺度时空变化特征 17
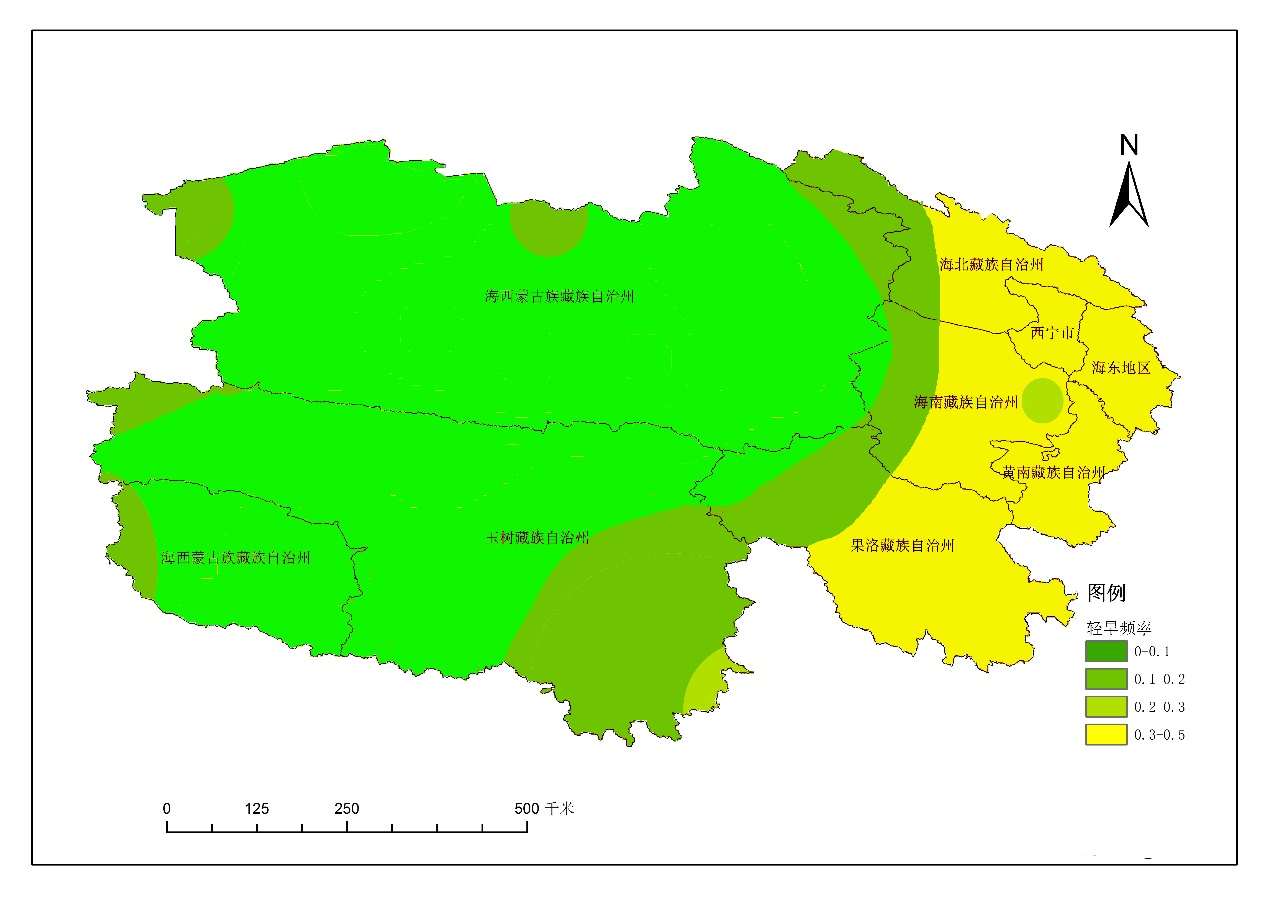
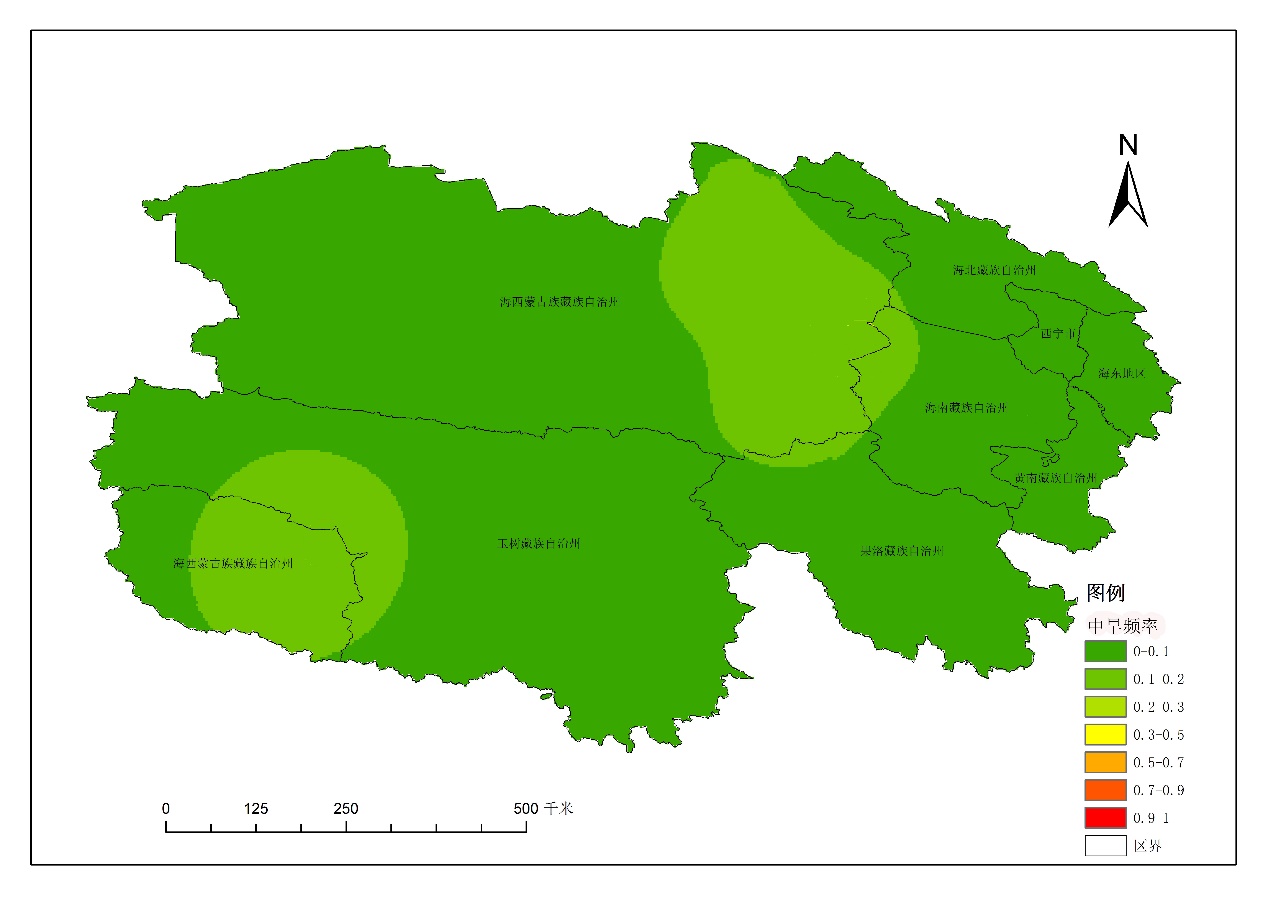
4.2.1季节尺度干旱发生频次的空间分布特征 17
4.2.2季节尺度干旱频次时间变化特征 19
4.2.3季节尺度干旱强度分布特征 21
5.结论与展望 21
5.1主要结论 21
5.2不足与展望 22
参考文献 24
致谢 26
近50年来青海省干旱时空变化分析
莫泽民
, China
Abstract: Qinghai Province in the country within a relatively special geographical location, climatic conditions, hydrological conditions, economic and social development level exacerbated the drought for some areas of the hazards and the impact of drought complexity, analysis of Qinghai Province, the spatiotemporal changes in the law of the future Of the drought warning, monitoring also has a positive effect. In this paper, the regional time span is relatively large. Therefore, the monthly precipitation data of 33 stations in the meteorological stations in Qinghai Province since 1961 are used to calculate the percentage of precipitation anomalies. Using the geographic information system, Perform contours and interpolations for specific values. Based on the precipitation data of the 33 meteorological stations, according to the "GBT20481-2006 meteorological drought grade", the percentage of precipitation anomalies (Pa) and the percentage of annual precipitation anomalies (Pa) were calculated for the past 50 years data. According to the drought grade index, the drought is divided into several grades, and the distribution maps and tables are made according to the seasonal scale and annual variation scale, and the temporal and spatial characteristics of drought in Qinghai Province are obtained.
In this paper, the regional time span is relatively large. Therefore, the monthly precipitation data of 33 stations in the meteorological stations in Qinghai Province since 1961 are used to calculate the percentage of precipitation anomalies. Using the geographic information system, Perform contours and interpolations for specific values. Based on the precipitation data of the 33 meteorological stations, according to the "GBT20481-2006 meteorological drought grade", the percentage of precipitation anomalies (Pa) and the percentage of annual precipitation anomalies (Pa) were calculated for the past 50 years data. According to the drought grade index, the drought is divided into several grades, and the distribution maps and tables are made according to the seasonal scale and annual variation scale, and the temporal and spatial characteristics of drought in Qinghai Province are obtained.
Key words: Qing Hai; PAI; Drought; Temporal and spatial features
1.绪论
1.1研究的意义和背景
干旱是指由于水分的收支不平衡或供求不平衡而形成水分短缺现象[1]。更加详细的表达,干旱就是水的需求量缺乏,即是一种长期以来降雨量很少或者无有效降水的一种特征,并且干旱的程度取决于水分需求的持续时间和需求量。目前国际上缺乏对干旱的标准通用定义,按照世界气象组织的定义,干旱是一种持续的、异常的降雨短缺。随着相关研究的深入,学界开始逐渐认识到降水量这一指标并不能完全表征干旱的全部特征,所以一些学者开始结合其他学科去衡量和探讨干旱问题。在实际的水分需求状况之中,影响水分的供需关系的因素非常多。影响水的供需包括降水量、蒸发量、气温、下垫面的径流量等自然因子,还有土地利用类型、人口密度、产业结构与分布、种植制度、基础设施状况等人文社会因素。
干旱是一种气候灾害,也是一种持续性的气象灾害[2-3]。气候干旱也可以叫做干燥,它是由于气候、海陆位置、地形等变化不大的因子在一些地方多年形成的水分缺乏状况。气象干旱也叫做大气干旱,它是由于各种大气因素,比如降水和气温的年际、季节、月份等时间变化从而形成的随机的异常的水分缺乏现象。气象干旱与气候干旱有一定的联系,但是两者不是等同的。气象干旱不光发生于半干燥、干燥的气候地区,也同样分布在降水量比较多的气候地区。干燥和湿润指的一般是某个地区常年的气候状况,我国按照水分的分布状况把气候划分为湿润、半湿润、半干燥、干燥等气候类型。因此干燥与气象干旱的区别不在于平均降水量的多寡,而在于降水量的波动幅度。在大多数情况下,干旱指的是气象干旱,本文所涉及的干旱时空变化分析,指的是气象干旱。
干旱是指由于长期降水量缺乏,无有效降水或降水少,造成土壤水分缺乏,作物水分平衡被打破的一种气象灾害 [4]。世界范围内,干旱是一种非常常见而且形成时间比较长的一种自然灾害。其发生的频率很高,陆地上约有35%的范围内,频繁的受到干旱灾害的影响。干旱分布在全球大部分地区,全球有100多国家和地区基本上每年都受到不同强度等级干旱的影响,其中亚洲的受影响范围非常广。干旱已经成为一个严重威胁着人类生存的环境问题。依据相关的统计数据,全球年尺度范围下,旱灾造成的经济损失高达约70多亿美元 [5]。据统计,在各类自然灾害造成的总损失中,气象灾害造成的损失约占85%,而干旱又占气象灾害损失的50%左右[6]。当前全球气候变化波动变大,气候因子影响日益复杂,有研究指出,在这一背景下,有些当前的干旱灾害会继续增加[7]。
长期以来,我国就深受干旱的影响。根据相关资料统计,十五世纪末到二十世纪中我国重大的干旱年就有五十一年。北方发生干旱的频率次数多,受灾面积大,而且多发生长时间的连续干旱,灾情严重。相比较而言,我国南方发生干旱的频率和危害性较小。比较典型的是:1483-1485年的旱灾;1527-1529年的北方大范围连续干旱;1585-1590年北方和长江流域的连旱;1637-1634年中国大范围连续干旱,波及两京十三省;1689-1692年中国大部分地区的多年连旱;1876-1878年的北方连续干旱;1900年全国特大干旱;1928-1929年全国性大干旱;1936年全国性大干旱;1942年严重干旱。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:22658字
相关图片展示: