论文总字数:30555字
摘 要
放眼全球,能源资源短缺,环境污染日趋严重,开发清洁的新能源来代替化石燃料成为一个亟待研究的方向。可再生能有由于其所具有的分布范围广大,不产生污染气体,可持续发展,储量丰富等一系列优点,使得世界上许多国家渐渐提高可再生能源在能源体系中所占的比重。尽管可再生能源的开发潜力非常大,但是在可再生能源的使用中,却不可避免的遇到了整体利用效率不高的问题。可再生能源由于其来源的不稳定性决定了其具有波动性和不确定性。如果不加以管理地直接将可再生能源发出的电量并入大电网中,必将造成大电网的不稳定乃至崩溃,后果十分严重。在微网中,可再生能源可以更好的发挥其作用,能够减少其与大电网之间冲突矛盾。可再生能源在微网中可作为分布式电源,和其他传统的发电方式互相结合,为用户提供所需的电能。需求侧管理技术日益发展,电气自动化水平不断增加,使得电网与用户的双向互动高效用电成为可能。主动负荷能够主动配合需求响应计划,控制其消耗电能的多少,也可以向电网反向输电,以此来获得经济收益。主动负荷如:电动汽车,作为一种类似于蓄电池的储能装置,能够在负荷高峰期间向电网输送电能,负荷处于低谷期间吸收电能,减少负荷峰谷差率,提高微电网的运行经济性。
本文将电动汽车作为主动负荷,提出了一个包含光伏电池(PV)、风力发电机(WT)、微型燃气轮机(MT)、燃料电池(FC)、蓄电池(BAT)和电动汽车(EV)以及常规负荷的微网最佳运行策略和机组组合实现运行成本最小化。经济优化目标函数考虑:各分布式电源的建设成本、运维成本、排放成本(排放的污染气体的治污费用,如N、或)。目标函数约束考虑:微电网的电源与负荷之间的功率平衡及五个分布式电源的出力约束。最后编程采用带有罚函数约束的遗传优化算法求解经济调度模型,通过对电动汽车不同充电方式(错峰填谷有序充放电调度模式和无序随机充电模式)的微网运行策略和运行成本对比可知:有主动负荷参与的微网调度,可以更好的消纳可再生能源,显著的削减电网运行成本,增加微网经济效益。
关键词:微网; 可再生能源; 电动汽车; 经济调度模型
Abstract
The current shortage of energy, energy supply security situation are increasingly severe. Renewable energy sources become an integral part of national energy system because of its wide distribution, potential development, clean, safe, sustainable use of, etc. However, due to the randomness and volatility of renewable energy, its overall utilization rate is not optimistic. Although the development of renewable energy potential is very large, but in the use of renewable energy encounter the problems that the overall efficiency is not high. The instability of renewable energy determines its volatility and uncertainty. If we connect renewable energy directly into large power grid without management, it will cause the instability of power grid and even collapse, the consequence is very serious. Micro-grid technology, can efficiently integrate new and renewable energy generation. New energy and renewable energy, may combine traditional power generation through Micro-grid technology, mutually complementary support for power users. Development of smart grid technology has also led to the demand response and realize both way interactive efficient power consumption. With the rapid development of both way smart power technology, power load increasingly are diverse and rapid develop, automation and control of electrical equipment continue to improve, a new energy management system (EMS) are being developed, active load appear user side. Active load resources are widely distributed in the grid, run flexible and adjustable, and its cost with respect to the conventional unit has obvious advantages. As active load that can take the initiative with the demand response programs developed by Electricity operators, can effectively consume distributed renewable energy (DRE), can significant increase economic benefits in Micro-grid. For example, The electric Vehicle act as a mobile energy storage device in the micro-grid, it is possible to charge the load in peak time and when the power load are in the nadir time the EV(electric Vehicle) are charged .
This paper presents a micro-grid containing Photovoltaic cell(PV), Wind turbines(WT), micro turbines(MT), fuel cells(FC), batteries(BAT) and electric vehicles(EV), assuming two typical electric car user behavior, namely electric vehicle sequence charge mode and no sequence charge mode. One of the problem of Micro-grid operation control is economic dispatch, it refers to meet the power balance and all distributed power output constraint conditions, so that the total operating costs of micro-grid is smallest, total operating costs including: the construction cost of each distributed power, operation and maintenance costs, emission costs (emissions of polluting gases pollution control costs,for example N、或). Finally a genetic optimization algorithm in economic dispatch model is programmed, some practical examples’ results are analyzed in different weather conditions and different electric car charging strategy. It represents the effectiveness of economic dispatch model and genetic algorithm optimization of micro-grid, namely ,active load can good consume renewable energy, and increase economic efficiency of micro-grid.
Keywords: micro-grid; renewable energy; electric Vehicle; economic dispatch
目录
第一章 绪论 1
1.1课题研究背景 1
1.2国内外研究现状 2
1.2.1微电网研究现状 2
1.2.2主动负荷研究现状 2
1.2.3主动负荷参与电网调度消纳可再生能源研究现状 3
1.3研究意义 3
1.4主要工作 4
第二章 微电源的调度模型 5
2.1光伏发电 5
2.1.1光伏电池等效电路 5
2.1.2光伏电池的输出功率 5
2.2风力发电 7
2.2.1风力发电原理 7
2.2.2风力发电机组输出功率 8
2.3微型燃气轮机 9
2.3.1微型燃气轮机的工作原理 9
2.3.2微型燃气轮机的经济性模型 10
2.4燃料电池 11
2.4.1燃料电池的工作原理 11
2.4.2燃料电池的经济性模型 12
2.5蓄电池 13
2.5.1蓄电池性能参数 13
2.5.2蓄电池经济调度模型 13
2.6小结 14
第三章 电动汽车模型 15
3.1电动汽车充放电功率 15
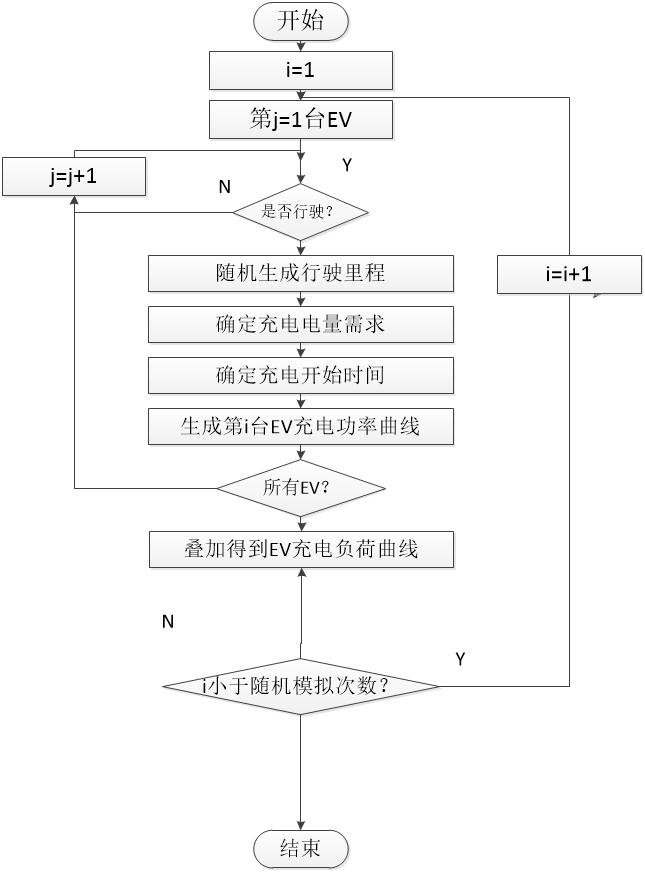
3.2随机充电模式下的电动汽车调度模型 16
3.3错峰充电模式下的电动汽车调度模型 20
3.4小结 20
第四章 微网经济调度模型 28
4.1运行策略 28
4.2目标函数 28
4.2.1目标函数 28
4.2.2目标约束 29
4.3算例分析 30
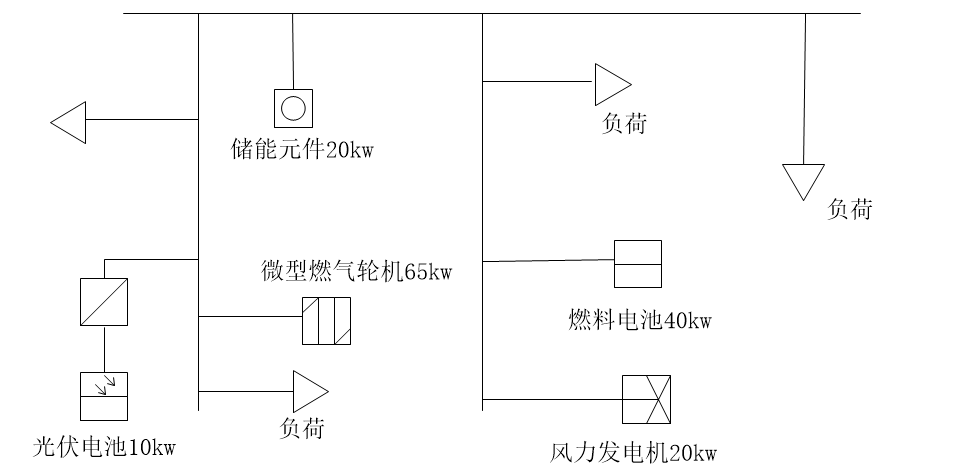
4.3.1算例模型概述 30
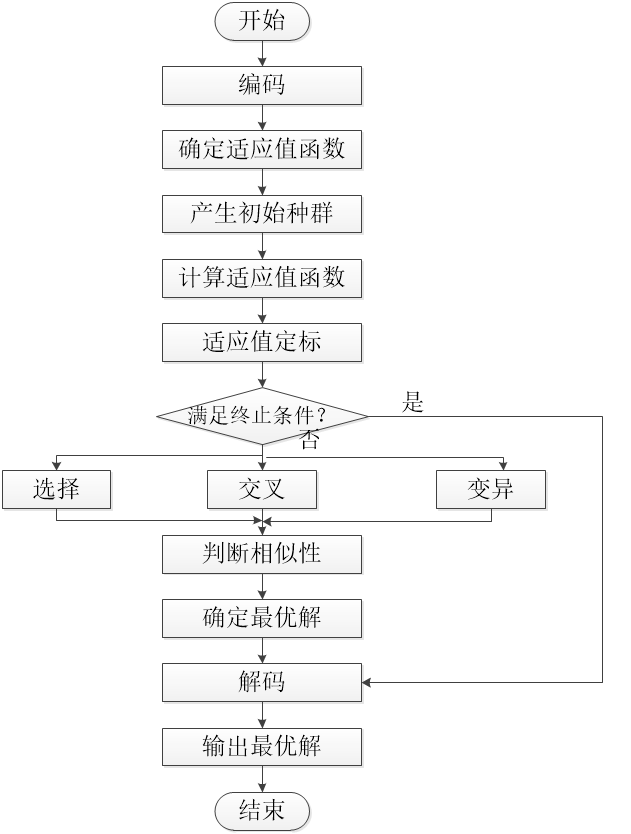
4.3.2优化算法 31
4.4优化结果 34
4.4.1电动汽车无序充电 34
4.4.2电动汽车有序充电 38
4.4.3结果分析 42
4.5小结 43
第五章 结论与展望 44
5.1结论 44
5.2展望 44
致谢 46
参考文献: 47
第一章 绪论
1.1课题研究背景
化石燃料为人类社会的发展提供了重要的能量,在过去的几个世纪了扮演了极其重要的角色。然而在国民经济和社会飞速发展的同时,对化石燃料的消耗也急速的增长,据统计,到2020年,煤炭的消耗量将要比2000年多出3倍。中国对化石燃料的消耗量非常大,并有逐年上升的趋势,但自身的开采量却不大,具体数据如表1.1所示。
表1.1 我国石油消费情况
年份 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
石油消费总量(亿吨) | 3.69 | 3.76 | 3.88 | 4.29 | 4.60 | 4.84 |
石油对外依存度(%) | 49 | 50 | 53 | 55 | 55 | 56 |
进口石油量(亿吨) | 1.81 | 1.88 | 2.06 | 2.36 | 2.53 | 2.71 |
然而化石燃料作为不可再生资源,如此大的化石燃料消耗使得化石能源的储存量缩减到了令人担忧的程度,国际能源形势也十分堪忧。此外,化石燃料的燃烧也造成了环境的恶化,产生污染的原因主要有:化石燃料在燃烧时没有与氧气充分反应,产生CO;碳粒、烟尘和没有完全燃烧的C、H化合物排放到空气当中;杂质燃烧时(如硫),产生SO2等毒害气体。在能源形势越来越严峻和环境污染越来越严重的大环境下,开发清洁的新能源来代替化石燃料为一个亟待研究的方向。
可再生能源由于具有资源分布范围广、开发潜力具大、可循环再生、清洁、安全等特点,越来越受到重视。充分发挥可再生能源的潜力,建立可持续发展的能源结构,逐渐用可再生能源代替传统的化石能源实现供电,成为了日后国家能源体系发展的趋势。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:30555字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


