论文总字数:17950字
目 录
0 引言…………………………………………………………………5
1 数据与方法…………………………………………………………5
2 结果与分析…………………………………………………………6
2.1 北极海冰范围的年际与季节变化 …………………………………………………6
2.1.1 北极海冰范围各季节的年际变化 …………………………………………6
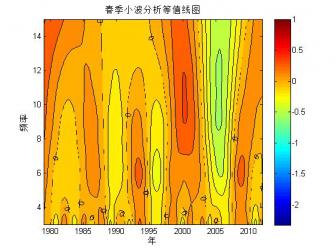
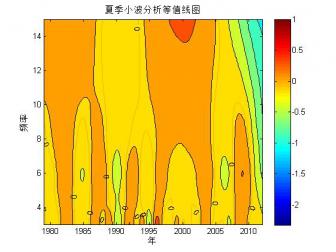
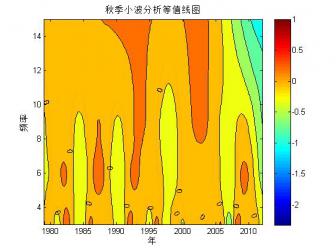
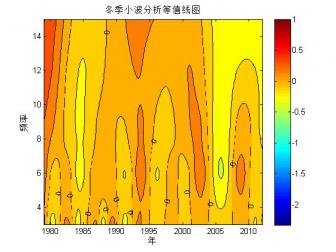
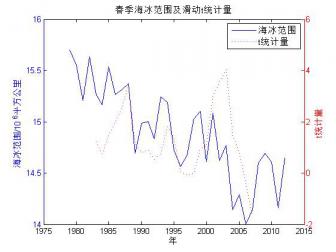
2.1.2 北极海冰范围的小波分析 …………………………………………………7
2.1.3 滑动t检验法检验北极海冰范围在春、夏季的突变 ……………………9
2.2 北极海冰的分布变化………………………………………………………………10
2.2.1 大西洋扇区和太平洋扇区不同季节海冰范围年际变化…………………11
2.2.2 东半球和西半球不同季节海冰范围年际变化……………………………13
2.3 北极海冰分布成因的初步分析……………………………………………………15
2.4 通过楚科奇海锚碇潜标数据分析北极海冰的范围变化和漂移现象……………17
2.4.1 2012年7-9月海冰范围的变化 ………………………………………… 17
2.4.2 楚科奇海锚碇潜标观测数据的分析………………………………………20
2.4.3 楚科奇海锚碇潜标观测结果对海冰范围变化的分析……………………22
3 结论 ………………………………………………………………23
4 讨论 ………………………………………………………………24
参考文献 ……………………………………………………………25
致谢 …………………………………………………………………26
北极海冰的季节与年际变化分析
崔子健
, China
Abstract: The Arctic is the cold pole of the Northern Hemisphere and it plays an important role in the regulation of global climate. With the melting of Arctic sea ice, the Arctic has attracted more and more attention. The multi-angle comparison and analysis of changes in the distribution and extent of Arctic sea ice over time using satellite remote sensing concentration data from the Arctic Sea Ice Monitoring (1979-2012) released by the American Ice and Snow Center; using the CTD data from China's fifth hydrological survey of the Arctic Sea, the impact of Atlantic and Pacific water injections on the distribution of sea ice in the Arctic Ocean was compared. By comparison we can draw: (1) Arctic sea ice has a decreasing trend in all seasons, and the decreasing trend in summer and autumn is more obvious around 2010; (2) With regard to the distribution of Arctic sea ice, the area of sea ice in the Western Hemisphere is approximately 1.5-2x106 km2 more than in the Eastern Hemisphere. However, there was a significant negative correlation between the changes in the area of the two hemispheres around 1998. Even in the autumn, the area of sea ice in the Eastern Hemisphere has exceeded the Western Hemisphere. (3) To further compare the interannual variations of the sea ice extent between the Atlantic sector and the Pacific sector, it can be seen that the extent of sea ice in the Pacific sector is more than twice that of the Atlantic sector; Interannual changes in the sea ice extent of the Atlantic sector show fluctuations in each season, while the winter and spring seasons in the Pacific sector do not show any significant reduction. In addition, according to the sea ice concentration distribution map published on the sea ice remote sensing website of Bremen University in Germany, it can be found that the sea ice in the Pacific sector of the Arctic Ocean drifts over time while the range changes. Using the observation data of the anchor submarine laid and recovered in the Chukchi Sea during the hydrological survey of the fifth Arctic Sea in China, it is further speculated that the sea ice extent and sea ice drift are related to the injection of Pacific water.
Key words: Arctic; Sea ice changes; Sea ice distribution; Sea ice drift
0 引言
北极包含北极圈内的海洋与相邻的有冰海域,总的来说,有七个边缘海、两个大型海湾、两个深海盆。边缘海有波弗特海、楚科奇海、东西伯利亚海、拉普捷夫海、喀拉海、巴伦支海和格陵兰海。两个海湾是哈德孙湾和巴芬湾。两个深海盆是加拿大海盆和欧亚海盆。除了这些边缘海、海湾、深海盆以外,北冰洋还有弗莱姆海峡、白令海峡和加拿大北极群岛的众多海峡。北冰洋通过格陵兰海和加拿大北极群岛与大西洋连通,通过白令海峡与太平洋连通。
北极是北半球的冷极,是北半球十分重要的冷源。其中北极的海冰又对全球的大气以及海洋环流有关键和持续的影响[1-4]。当前预测和分析全球的气候变化趋势关键之一,就是准确地获取北极海冰的变化趋势信息,再进行研究分析,进而总结全球气候变化对海冰的影响[5]。
北极是一个能敏锐感知全球变暖影响的地方,北极变暖的速度是北半球变暖平均速度的2倍,这被称为北极放大效应。Rune 等[6]认为大气热量输送的变化可能是最近北极温度放大的一个重要原因,近期地球表面的变暖很可能是由于大气温室气体浓度的增大。Hansen等[7]认为虽然在全球范围内大多数温室气体分布相当均匀,但是极地地区对温室气体增温的响应比赤道地区大。这种响应取决于气候系统内的各种反馈。除了冰和雪作用的物理过程,大气的分层也构成了这样的反馈。在极地地区,对流层的分层相较于赤道地区更加稳定[8]。而James 等[9]认为海冰的减少在最近的北极放大效应中起到了主导作用。
1970年以来,越来越多的研究人员开始利用卫星的观测资料研究北极的海冰变化。大部分的研究表明,自卫星观测以来,北极的海冰覆盖范围便处于波动减少的趋势,而这种趋势在1990年以后更加明显[5]。Parkinson等[10]通过SMMR和SSMIS的海冰密集度数据分析了1979-2010年北极的海冰变化,分析结果显示北极的海冰覆盖范围以每10年-4.1%±0.3%的速率减少(白令海有并不显著的增长)。武炳义等[11]研究表明:北极各海区海冰面积都存在年际变化,同时存在年代际时间尺度变化,如春季的格陵兰海冰存在12年变化周期,冬、春季节的喀拉海和巴伦支海的海冰则存在10年变化周期。
北极海冰覆盖范围加速减少的同时,“东北航道”的开通也逐渐被人们所重视。东北航道即位于东半球亚欧大陆的北岸的一条海上航道,东北航道的开通,对于我国国际贸易和沿海经济发展将产生深远影响。张侠等[12]认为,与传统的航线相比,东北航道将使上海以北的港口到北海、波罗的海、欧洲西部等港口的航程缩短25% ~ 55%。东北航道的开通, 将极大拉近东亚和欧、北美等市场的距离, 促进国际分工和产业格局发生变化。
本文利用中国北极海域水文考察的CTD数据以及海冰密集度数据,从时间和空间的角度对北极海冰密集度进行对比和分析,并对太平洋扇区的大尺度海冰漂移现象进行总结和分析。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:17950字
相关图片展示: