Table of contents
Abstract 3
1. Introduction 4
2. Materials and methods 5
2.1 MARGA instrument 5
2.2 Sampling site 6
3. Results and Discussions 7
3.1 Equilibrium properties of water-soluble ion species 7
3.1.1 Balance of total cation and anion in aerosol 7
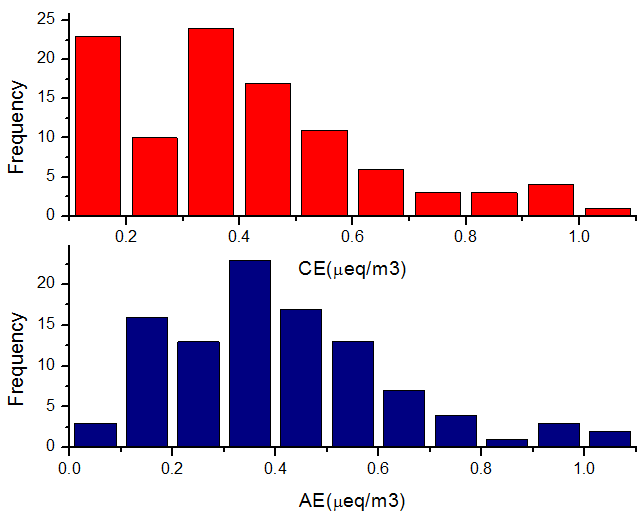
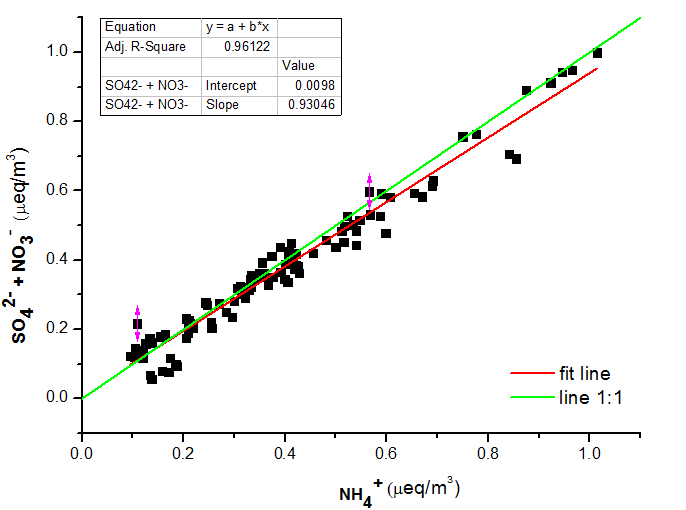
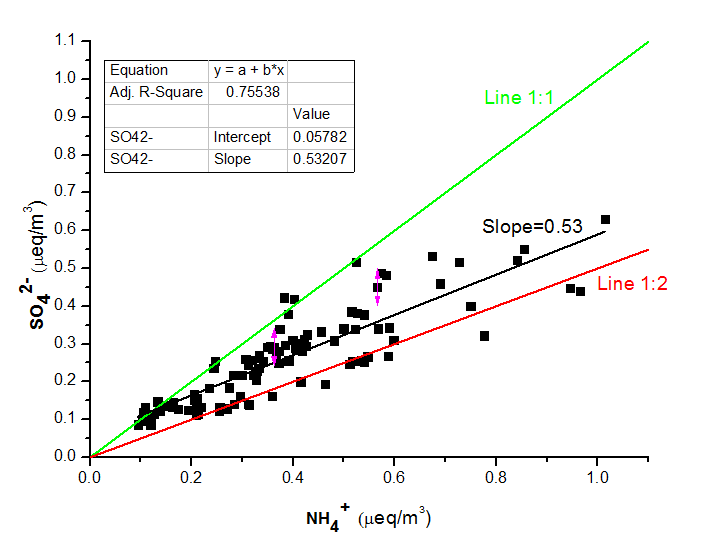
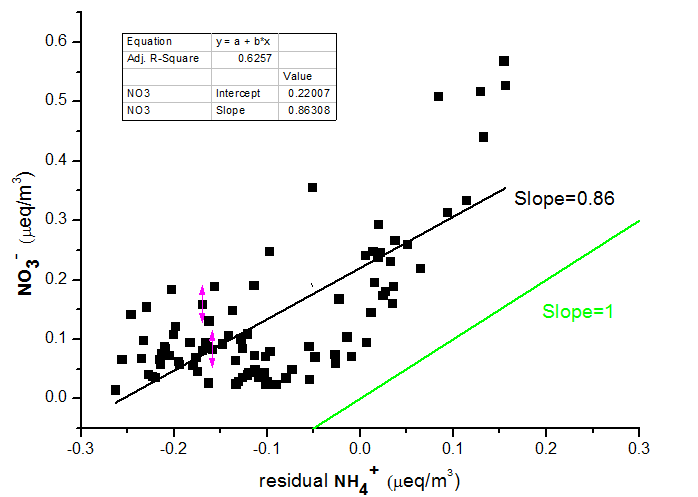
3.1.2 The correlation between NH4 、NO3- and SO42- 8
3.2 Concentration characteristics of water-soluble ion species 12
3.2.1 Total concentration of water-soluble ion species 12
3.2.2 Diurnal profiles of water-soluble ion species 15
3.2.3 Effects of different weather conditions on water-soluble ion species 18
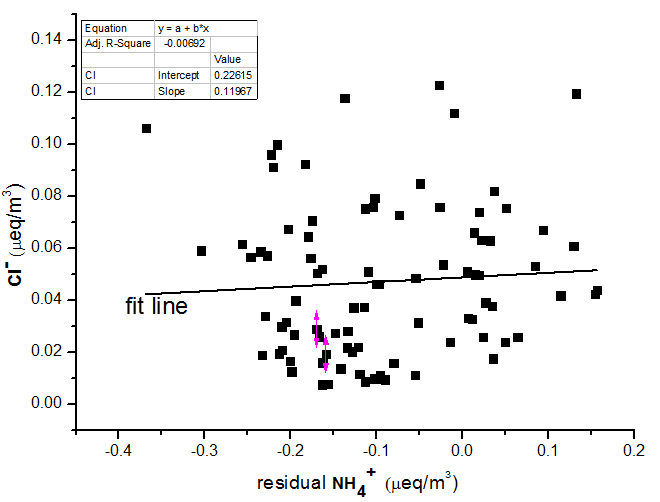
3.3 Gas-particle equilibrium between water-soluble ion species and the precursor gases 20
4. Conclusions 21
References 22
Acknowledgments 24
Study on water-soluble ionic composition of
aerosol during summer over Nanjing
Jiayi Cai
School of Atmospheric Physics, NUIST, Nanjing 210044, China
Abstract:In this paper, the physical and chemical characteristics of water-soluble ions in aerosol in Nanjing city are studied by using MARGA data with high temporal resolution. The results showed that the positive and negative ions of aerosol in Nanjing fitted well and the square of correlation coefficient was up to 0.967. During observation period, NH4 mainly combined with SO42- to form (NH4)2SO4, followed by NH4HSO4 and NH4NO3, while the combination form NH4Cl was a little. The mass concentration of 8 kinds of water-soluble ions in aerosol and the total concentration of PM2.5 maintained a high degree of consistence. The secondary ions SO42-, NH4 , NO3- accounted for 57.57% of the whole water-soluble ions, which were the main component of PM2.5 in Nanjing. The proportion of mass concentration of SO42- was the largest in water-soluble ions, which increased with the increase of air temperature and decreased with the increase of humidity, while the proportion of NO3- was the opposite, which increased obviously with the increase of humidity. Diurnal variation study showed that during the daytime SO42- concentration in Nanjing was slightly higher than that in the evening, and the diurnal ratio was 1.14, while situation was different when came to NO3-, the ratio of which was 0.937. There was a significant correlation between SO2 and SO42-, NH3 and NH4 in Nanjing atmosphere, but the correlation between HNO3 and NO3-, HCl and Cl- were not clear.
Key words:the Nanjing city, MARGA, water-soluble ions, PM2.5, aerosol
1. Introduction
Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) is not a simple component of air pollution but a complex and volatile air pollutant, which can be divided into primary particles and secondary particles. Most of primary particles directly discharge from the pollution sources, like elemental carbon (EC), organic carbon (OC) and soil particles. Secondary particles are produced by a variety of gaseous pollutants discharging from the pollution source through a series of complex physical and chemical changes, like Nitrate, sulfate, ammonium salts, and other organic compounds. PM2.5 in the atmosphere, due to its small particle size and large surface area, is easy to accumulate toxic and harmful substances in the air and can enter human’s body when human breath. Moreover, it can enter human’s alveolar or blood circulation system, which directly lead to cardiovascular diseases and respiratory diseases. As one of the most complicated and harmful pollutants in the atmosphere environment, it not only has great harmfulness to human health and life, but also results in reduced visibility, acid deposition, climate change, photochemical smog and other major environmental problems. The chemical constituents in atmosphere according to different solubility can be divided into the water-soluble and the insoluble. The water-soluble ions include SO42-, NO3-, NH4 , Cl-, K , Ca2 , Na , Mg2 , NO2-, PO43-, C3H4O4 and so on. In recent years, the proportion of water-soluble ions in the urban atmosphere PM2.5 has been very high, and it increases along with the decrease of particle size, which account for 80% in the range of 0.1~ 0.3 μm (Hu et al., 2009). Cl-, NO3- and SO42- in the atmosphere are the main soluble anionic acid ions, which can become CCN easily and indirectly affect climate by changing the distribution and optical characteristics of cloud droplets (Charlson et al., 1992). Sulfate, nitrate, ammonium salts and other components in PM2.5 have a significant impact on urban visibility and the correlation between SO42-, NO3-, NH4 and light scattering is much higher than that of other components (Waston et al., 2002). Therefore, it is helpful for us to understand the source and formation mechanism of the fine particulate matter in the air by analyzing the change characteristics of the water-soluble ions components, especially SO42-, NO3-, NH4 and other secondary ions.
Numerous studies have focused on identifying the physical and chemical properties of water-soluble ions in aerosol. Recently, an increasing NO3 - contribution and a decreasing SO42- contribution to PM1 mass loading with elevated PM1 mass concentration were reported in Shanghai (Yang et al., 2014). Besides, the nitrate content in aerosol of one German city (Meptitz) was distributed both in the coarse and fine particles, while the sulfate mainly existed in the fine particles (Maenhaut et al., 2002). In demostic, the physical and chemical properties of aerosol in the Pearl River Delta were studied by using MARGA ion on-line analyzer, and the influence of fine particle pollutants on the degradation visibility of the Pearl River Delta was investigated with water-soluble ion composition spectrum (Wu et al., 1994). Under the premise of basically stable pollution source, weather condition is the main factor that decide the air quility. Temperature, relative humidity, precipitation and other meteorological factors have an important influence on the diurnal variation of PM2. 5 daily average concentration (Tai A P K et al., 2010). Stratification stability, static wind and temperature inversion are favorable to the accumulation of pollutants, the increase of aerosol and the decrease of visibility (Zhou G, 2014).
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:56182字
相关图片展示: