论文总字数:23315字
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract II
1 引言 1
1.1 研究目的与意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状 1
2 研究区域 2
2.1 区域概况 2
2.2 资料选取 2
3 研究方法 3
3.1 水文变化指标( IHA) 3
3.2 水文变化范围法( RVA) 4
4 结果与分析 5
4.1径流变化特征分析 5
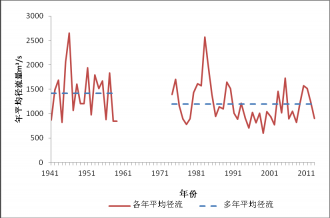
4.1.1年尺度径流变化特征 5
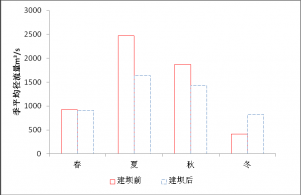
4.1.2季尺度径流变化特征 6
4.2 基于RVA方法的日径流变化特征分析 7
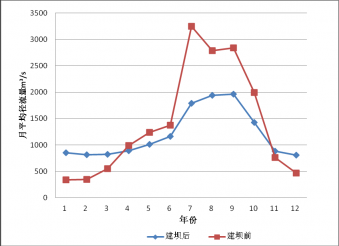
4.2.1 月平均径流量变化分析 8
4.2.2 径流量极值变化分析 10
4.2.3 径流量极值时间变化分析 11
4.2.4 高脉冲和低脉冲出现的频率和历时 11
4.2.5 涨洪落洪的比率及频率 12
4.2.6 整体水文改变度 13
4.3建坝后径流变化特征分析 13
4.4水位变化特征分析 20
4.5原因初探 22
4.5.1 人类活动因素 22
4.5.2 气候变化因素 24
5 总结 25
参考文献 25
致谢 28
人类活动对汉江下游水流情势的影响
巫晓燕
, China
Abstract: Since the founding of new China, with the development of China's economic construction, the demand for water resources has gradually increased. The development of water conservancy and urbanization has changed the natural state of the river channel and destroyed the balance of the river ecosystem. The Han River is the largest tributary of the Yangtze River and this paper selects 1941-2013 from middle and lower reaches of Hanjiang River in Xiangyang hydrological station water runoff data, using hydrological index method (IHA), hydrological change range method (RVA), and Mann-Kendall nonparametric test to quantitative assessment that the impact of human activities on the flow regime in the lower Hanjiang River. The study found that the impact of human activities on the hydrological situation in the lower reaches of the Hanjiang river can be divided into three periods:1941 - 1960 for the early dam;1974-1991 for the early mutation;1991 - 2013 for the late mutation. The average runoff of the lower reaches of the Hanjiang River decreased by 15%,the runoff was reduced by 31% in the flood season and increased 111% in the dry season, and the runoff is evenly distributed throughout the year. The frequency and duration of floods were obviously reduced, and no floods occurred after 2005.Through the RVA evaluation, the overall hydrological change in the lower reaches of Hanjiang River is moderate change. Furthermore, the change of the water level of Xiangyang station is analyzed and it is found that stage discharge relation of Xiangyang station changed after the construction of the dam. Then we selected 1958, 1983 and 2005 as the representative years to draw the stage discharge curve. It is found that when the flow is less than 14000m3/s,the same flow corresponding to the water level has been reduced after the construction of the dam. It shows that the construction of Danjiangkou reservoir has a significant impact on the water flow in the middle and lower reaches of Hanjiang River, and has caused a certain degree of damage to the function and stability of the ecological environment in the middle and lower reaches of the Hanjiang river. At the same time, urbanization, industrialization, population growth and climate change also have an impact on the change of water flow in the lower reaches of the Han river. It is hoped that this paper can provide the scientific basis for the ecosystem protection and reservoir dispatching of the lower reaches of Hanjiang River.
Key words: Hanjiang River; human activities; Range of Variability Approach
1 引言
1.1 研究目的与意义
近几十年以来,伴随着我国急剧增长的人口数量与快速发展的社会经济,我国的水资源的需求也在逐步增加。水是一种宝贵的自然资源,不仅是所有生灵的源泉,也是一种天然的清洁能源。由于我国幅员辽阔、气候环境与地理环境复杂,水资源在时空分布上呈现出明显的不均匀性,并不能满足不同地域人民生活与经济建设对水资源的需求,水资源的合理开发是我国解决水资源矛盾的必经之路。新中国成立以来,我国在各大流域进行了修建水库、引水灌溉等大量的大规模水事活动,如长江三峡水库、南水北调工程等。
据2013年第一次全国水利普查统计,我国库容10万m3及以上的水库工程共98002座, 总库容9323.12亿m3,约控制着河流34.4%的径流量[1]。2014年三峡水库全年累计发电988亿kw•h,成为世界上年度发电量最高的水电站,减少了近一亿吨二氧化碳排放和4900多万吨原煤消耗,相当于武汉市两年半的用电量。
水库的建设开发对我国经济建设具有重大意义,在发挥蓄水、防洪、调度区域水资源、发电等重要作用的同时,水库的建设也改变了河道的天然状态,对河流的水流情势、河水水质、周围地貌以及生态环境产生了不利影响。水流情势影响着河流生态系统许多方面,包括河流物质循环、能量交换、生物自然栖息地条件等,生物的栖息地条件与流域物种的分布、种类有直接联系,水库的修建将影响流域的物种多样性 [2]。水库建设造成的生态问题正在显现,水库修建导致鱼类品种及数量减少、水库蓝藻爆发湖水一夜变绿等事件频频爆发。
随着公众生态环保意识的逐渐提高和河流生态问题的日益显现,人类活动对河流生态环境的影响受到越来越多的关注。本文旨在通过对汉江下游水流情势特征变化的评估,揭示人类活动对汉江下游河流生态环境的影响,为汉江下游河流生态环境保护和水库调度工作提供科学依据。
1.2 国内外研究现状
20世纪以来,关于人类活动对河流的影响已经引起国内外学者广泛的讨论。水利工程的修建一定程度上改变了天然河道的自然特征,如何定量评估大坝下游水流情势变化的研究成为国内外学者研究的前沿领域。
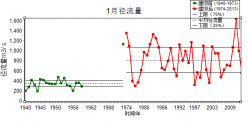
基于统计学分析,目前在径流序列的趋势与突变现象检验中,现在常用的方法主要有以下几种:克拉默法(Cramer)、滑动 t 检验、曼-肯德尔法(Mann-Kendall)、勒帕热法(Lepage)、有序聚类法、佩蒂特法(Pettitt)、山本法(Yamamoto)和启发式(BG)分割算法等。Mann-Kendall非参数检验法适用于非正态分布的时间序列,尤其是水文及气象数据。本文也将采用此方法对汉江下游断面径流变化做趋势和突变分析。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:23315字
相关图片展示: