论文总字数:20558字
目 录
1 引言 1
2 资料与方法 1
2.1资料来源 1
2.2大气稳定度研究方法 1
2.2.1 温差法 2
2.2.2 温差—风速法 2
3 环境空气污染物浓度的影响 3
3.1 近两年京津冀区域主要大气霾污染物浓度变化情况 3
3.2 京津冀区域代表城市2015年12月大气霾污染过程描述 3
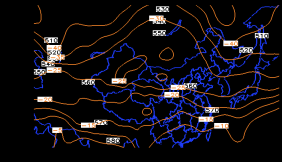
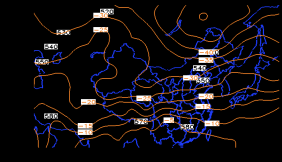
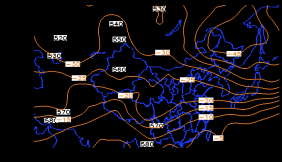
4 天气形势分析 5
4.1 高空环流形势 5
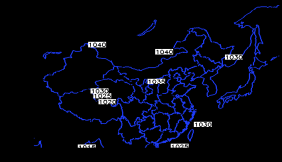
4.2 地面天气形势 6
5 低层大气层结稳定度分析 7
5.1 温差法、温差—速度法对比分析 7
5.2 逆温层 9
5.3 垂直速度场 10
5.4 地面风场 11
6 水汽条件与地形效应 11
6.1 水汽条件分析 11
6.2 地形阻挡作用 13
7 结果与讨论 14
参考文献 15
致谢 17
2015年12月京津冀雾霾污染天气过程分析研究
田雨
,China
Abstract:The formation of haze pollutions in late december 2015 over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region is analyzed based on the air quality monitoring data, daily meteorological data and reanalysis data.The results show that the pollutant concentration has severely exceeded standard in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during the haze days. has reached a hazardous level of 143
has reached a hazardous level of 143 in december 2015,an increase of 44.4% from the same period of last year.And
in december 2015,an increase of 44.4% from the same period of last year.And  has reached 206
has reached 206 ,an increase of 23.4%.High concentrations of contaminant particles becomes an important reason for the strong haze outbreak. During this haza event,the primary pollutants is
,an increase of 23.4%.High concentrations of contaminant particles becomes an important reason for the strong haze outbreak. During this haza event,the primary pollutants is and the two peak of this haza process is 20-21th and 23-24th of December.In 500hpa aerial,the large-scale circulation impacting this haza event is zonal.During the first peak,Beijing-Tianjing-Hebei area locates at the bottom of ground high pressure,easterly winds blowing from the sea containing a large number of aerosol particles successively through Tianjin, Chengde, to Beijing, Baoding and other places.And pollutants converge in Beijing,Baoding because of Yanshan, Taihang’s blocking effect.During the second peak, contaminant particles from Baoding, Shijiazhuang converge with high humidity aerosol particles from the sea in Mountains and Plains conjunction place.Result in Beijing, Baoding, Langfang and other regions’s locating in the junctional zone occurring second peak. Large quantities of pollutants gathered in Beijing which locate at the corner of Taihang and Yanshan Mountans,while Tianjin dosen’t undergo secondary haze peak because of terrain flat and being the mouth of the sea. Since the Yanshan mountain’s barrier of southwest wind’s transport of pollutants, Zhangjiakou always have a high air quality. During this haze period,inversion layer exist in the lower troposphere over the north central region of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and the top of inversion layer is between 950-850hpa.The exist of inversion layer lead to atmosphere quiet steady, with the daily average wind speed less than 2m/s and relative humidity around 50% to 90% near the ground, the lower atmosphere is favorable to haze formation. After 25th, the vertical movement of the lower atmosphere enhance, surface wind speed increase significantly, haze process coming to an end.
and the two peak of this haza process is 20-21th and 23-24th of December.In 500hpa aerial,the large-scale circulation impacting this haza event is zonal.During the first peak,Beijing-Tianjing-Hebei area locates at the bottom of ground high pressure,easterly winds blowing from the sea containing a large number of aerosol particles successively through Tianjin, Chengde, to Beijing, Baoding and other places.And pollutants converge in Beijing,Baoding because of Yanshan, Taihang’s blocking effect.During the second peak, contaminant particles from Baoding, Shijiazhuang converge with high humidity aerosol particles from the sea in Mountains and Plains conjunction place.Result in Beijing, Baoding, Langfang and other regions’s locating in the junctional zone occurring second peak. Large quantities of pollutants gathered in Beijing which locate at the corner of Taihang and Yanshan Mountans,while Tianjin dosen’t undergo secondary haze peak because of terrain flat and being the mouth of the sea. Since the Yanshan mountain’s barrier of southwest wind’s transport of pollutants, Zhangjiakou always have a high air quality. During this haze period,inversion layer exist in the lower troposphere over the north central region of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and the top of inversion layer is between 950-850hpa.The exist of inversion layer lead to atmosphere quiet steady, with the daily average wind speed less than 2m/s and relative humidity around 50% to 90% near the ground, the lower atmosphere is favorable to haze formation. After 25th, the vertical movement of the lower atmosphere enhance, surface wind speed increase significantly, haze process coming to an end.
Key words: severe haze events; Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region; meteorological conditions: large scale circulation, topographic effect
引言
大气霾过程直接影响着低层大气空气质量、有效能见度、直接和间接太阳辐射和生态系统等[31-32],与人类生产、生活息息相关。研究表明,PM2.5及更细小的细模态颗粒可渗透进人体支气管和肺部[33],长期暴露在高PM2.5环境中会大大增加呼吸系统疾病发病率[34]。除对人体健康的巨大影响外,大气中悬浮颗粒物还通过吸收和散射太阳直接辐射、作为云雨滴增长时的凝结核等方式影响着全球天气系统和水循环[35]。自然条件下霾天气的发生通常具有地域性,并且不受城市或者工业区的限制[1],近年来我国中东部地区霾污染天气频发,了解环境大气中浮游干颗粒物浓度、局地动力、热力过程、局地地形山脉阻挡等项对强霾过程发生的作用,是高效调节环境质量的重中之重。
京津冀区域地处华北平原北端,西临太行山、北倚燕山,是近年来国内经济高速发展的区域之一,也是重度霾污染频发的区域之一。2015年末,京津冀各城市AQI指数普遍居高不下,中国环境监测总站于2015年12月发布的重点城市空气质量状况报告[2]显示,根据环境空气质量标准(GB3095-2012)[3],京津冀13城市平均月空气质量达标天数仅占当月34.9%,超标天数中首要污染物PM2.5浓度达到 ,同比上升44.4%,是京津冀地区继2013年1月强霾事件以来,爆发的又一次重霾事件。
,同比上升44.4%,是京津冀地区继2013年1月强霾事件以来,爆发的又一次重霾事件。
本文针对2015年12月中下旬京津冀区域一次持续性灰霾过程,从环境空气颗粒物浓度变化、大气环流形势以及相关气象要素等方面进行诊断研究,以期为霾污染灾害过程预报提供参考信息。
资料与方法
2.1资料来源
常规气象资料来源于2015年12月1-31日国家气象局气象信息综合分析和处理系统(Meteorological InformationComprehensive Analysis and Processing System,MICAPS),及同期NCEP(National Centers for Environmental Prediction)CFSv2(Climate Forecast System Reanalysis Verson 2)再分析数据,包括位势高度、垂直速度、经纬向风分量和相对湿度等,MICAPS资料水平分辨率为2.5°*2.5°,CFSv2资料水平分辨率为0.5°*0.5°。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:20558字
相关图片展示: