论文总字数:21179字
目 录
1 引言...................................................1
2 资料及方法.............................................2
2.1模式设置.............................................2
2.2 排放源介绍...........................................3
2.3 使用数据说明..........................................3
3 模拟结果检验...........................................4
3.1 数据对比.............................................4
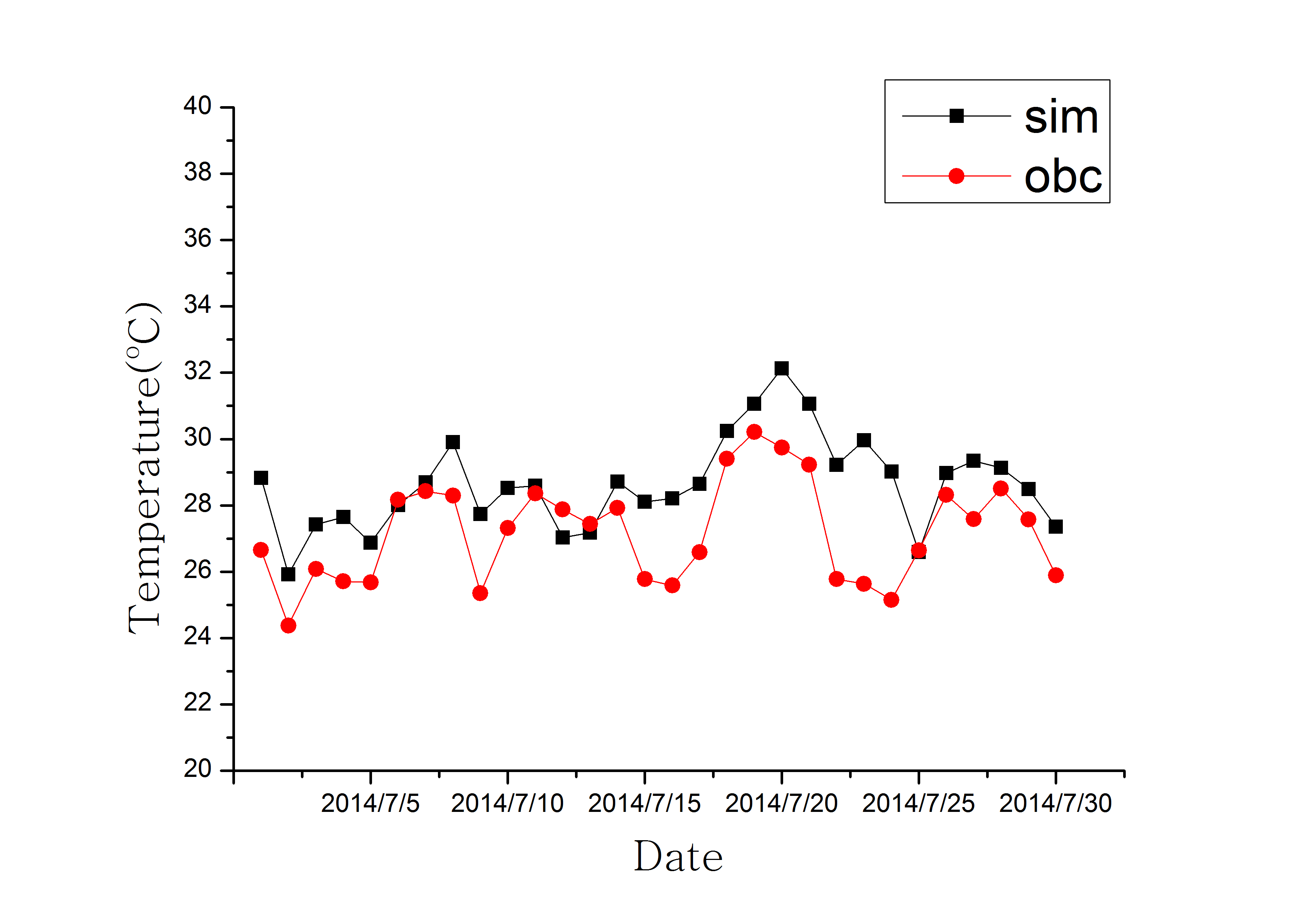
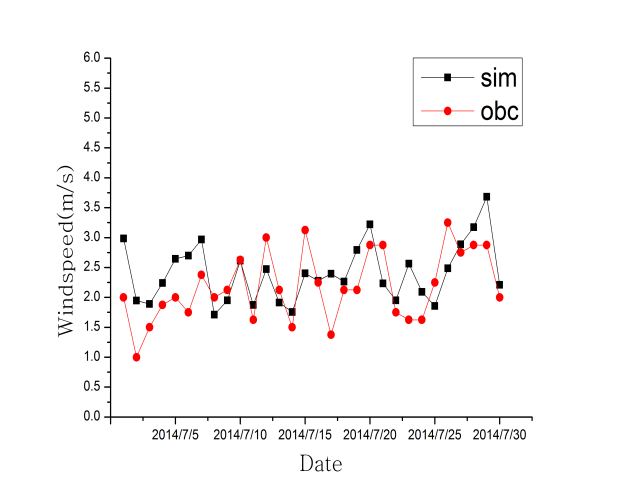
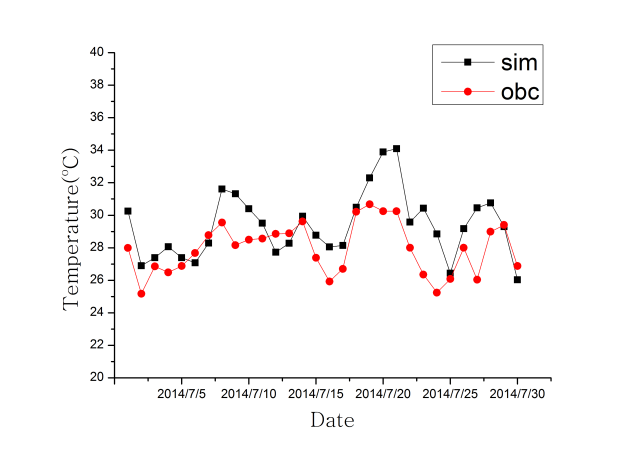
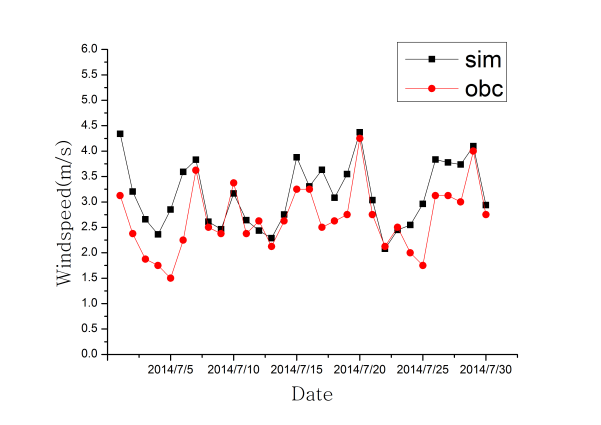
3.1.1 温度和风速.......................................4
3.1.2 月变化..........................................6
3.1.3 日变化...................................... ...8
3.2 模拟结果............................................10
3.2.1 月变化.........................................10
3.2.2 日变化.........................................14
4 京、津、冀对比分析....................................15
4.1 月变化对比分析........................................15
4.2 日变化对比分析........................................19
5 结论..................................................21
参考文献................................................21
致谢....................................................23
京津冀PM2.5变化特征的数值模拟与观测对比分析
赵汝悦
Abstract:Haze pollution as the most important area of Beijing, Tianjin weather occurs most frequently area, production and life of the people suffered that it can not function properly. Countries are also content as the PM2.5 air quality testing, evaluation system is an important indicator, real-time release relevant information to the public. This article will WRF-chem model schema validation study of the application of the model to simulate the data focused on the variation characteristics of PM2.5 and make comparative analysis of the observed variation in the three regions of PM2.5 , and then analyze its peaks and valleys the cause value. Preferred mode to capture the monthly variation of PM2.5 , correlation coefficient of 0.992; partial peak overestimated PM2.5 mass concentration observed, on average overestimated 5.073μg / m3 . Compared to five sites in Baoding, Beijing better simulation results, a correlation coefficient of 0.86 in Baoding, 0.81 in Beijing; correlation coefficient of only 0.38 Tianjin. Variation in simulation mode day, the performance of the PM2.5 mass concentration variation over time, the correlation coefficient was 0.54; and the observed results of PM2.5 mass concentration 24 hours compared to the simulation of the variation coefficient is smaller, observation diurnal variation of PM2.5 mass concentration compared to model simulations to be more stable. Wherein the analog-to-day changes in Zhangjiakou best correlation coefficient of 0.82, the average overestimation and observations 24μg / m3 . Simulation mode has the observed atmospheric haze of pollutants and the changing characters of Beijing, Tianjin region of great significance, not only to play a leading role in cognitive haze pollution, but also for control of the region upstream of the role of haze pollution reached base.
Key words:Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei;PM2.5;Change characteristics
1 引言
2013年9月13日,国务院颁布了《大气污染防治行动计划》,将京津冀重霾地区的大气污染的防治行动计划提上日程,计划要求京津冀地区2017年PM2.5浓度比2012年下降25%,北京市PM2.5年均浓度控制在60μg/m3左右的目标【1、11】。由此可见对于京津冀PM2.5的变化特征的研究必要性,为其大气污染的预防与治理工作提供基础的上游服务。
近年来,我国中东部地区空气重污染现象频发,并呈现复合性、区域性、周期性【2、23】。PM2.5是造成空气重污染的主要污染物。PM2.5是粒径较小的颗粒物,又称细粒子,对人体健康的危害及对环境的污染在颗粒物中最为突出【17、18】。研究表明由于PM2.5颗粒直径小且表面积大,易携带大量工业废气等有毒有害物质,对空气质量造成重要影响【22】。
PM2.5 的主要成分是SO42-、NO3-、NH4 、有机物、矿物质和元素碳【19-21】。而扬尘、二次反应(生成硫酸盐和硝酸烟)、燃煤、化石燃料燃烧等是 PM2.5气溶胶的主要来源【19-21】。为满足对于京津冀地区霾研究和控制的迫切要求,国内学者梳理了近年年来京津冀地区霾的长期变化特征、天气学特征、污染物来源等相关研究成果。主要从霾成因机制着手,并着眼于源解析和源谱,认为建立和完善我国本土的源谱乃当务之急。PM2.5 源谱对于建立PM2.5 中各组分的排放清单、定性识别污染类型、源解析和探究PM2.5 大气化学反应过程具有重要意义【3】。还总结出:北京PM2.5浓度变化特征的分析是分别从时间和空间上对北京的PM2.5浓度变化特征进行规律总结,得出在时间上北京市PM2.5浓度:春、冬两季较高,夏、秋两季较低的季节变化规律,以及“双峰双谷型”的日浓度变化规律;在空间上:水平方向无明显变化,竖直方向上随高度升高而下降,距离交通要道越近的地方PM2.5浓度越高【4】。
为进一步探究PM2.5浓度变化特征,由美国海洋和大气管理局、美国大气中心开发的WRF-chem[5]模式被许多国内学者在研究中投入使用,即一种耦合的空气质量模式系统。该模式中的气象模块和化学模块使同一坐标系。该模式是气象模式和化学模式完全在线耦合的。次网格传输使用相同的物理参数化方案,且无时间插值。当前的WRF-chem模式不仅具有WRF模式的完整功能,同时还可用于预测和模拟,例如温度场、风场、云雨过程等物理量的天气或气候。该模式还能通过天气预报和扩散模型的耦合来模拟排放和传输的成分,耦合天气、扩散、包含完整化学物中的空气质量模型来模拟PM颗粒物、O3等物质及辐射的相互作用等。作为空气质量模式的主要发展方向之一,WRF-chem模式在区域空气污染研究方面有较多应用[6-8]。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:21179字
相关图片展示: