论文总字数:15891字
目 录
1 引言 3
1.1 研究目的 3
1.2 国内外研究进展 3
1.3 主要研究内容 3
2 实验介绍及数据处理 3
2.1 观测实验 4
2.2 数据处理 4
2.2.1 数据处理步骤 4
2.2.2 归一化标准差 5
2.2.3 湍流通量 5
3 城、郊湍流宏观量对比研究 5
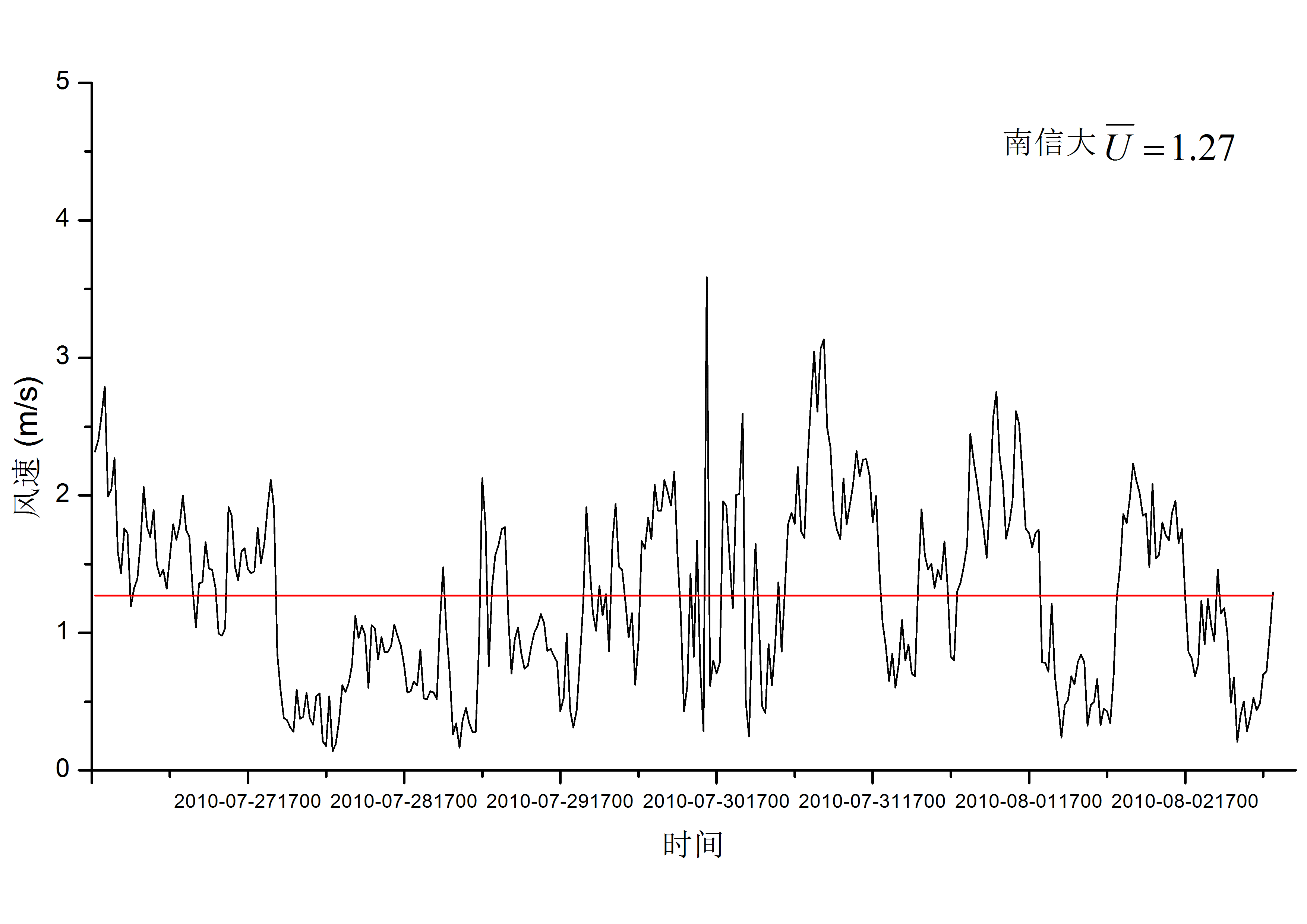
3.1 平均风对比分析 5
3.1.1 总体变化趋势对比分析 5
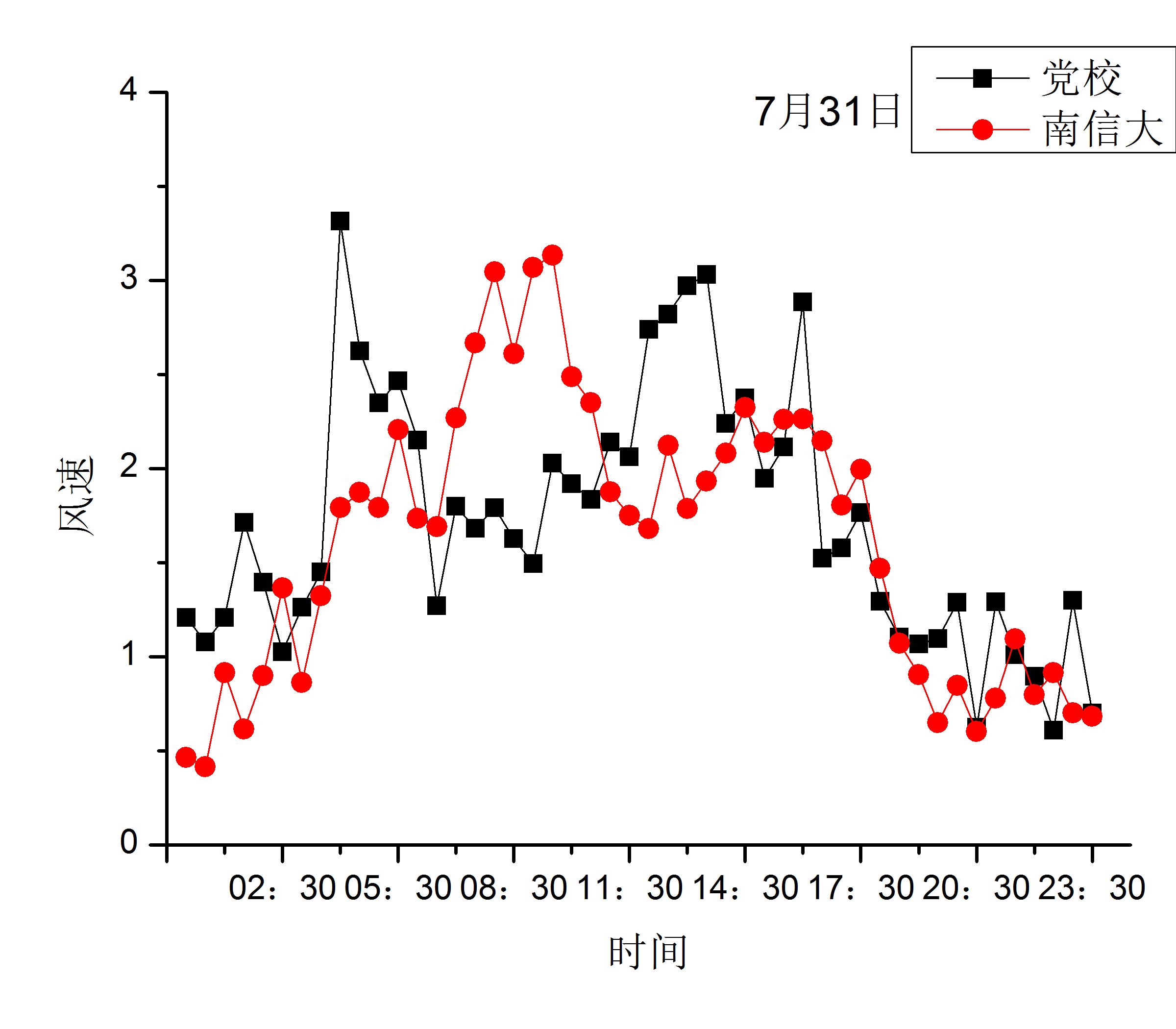
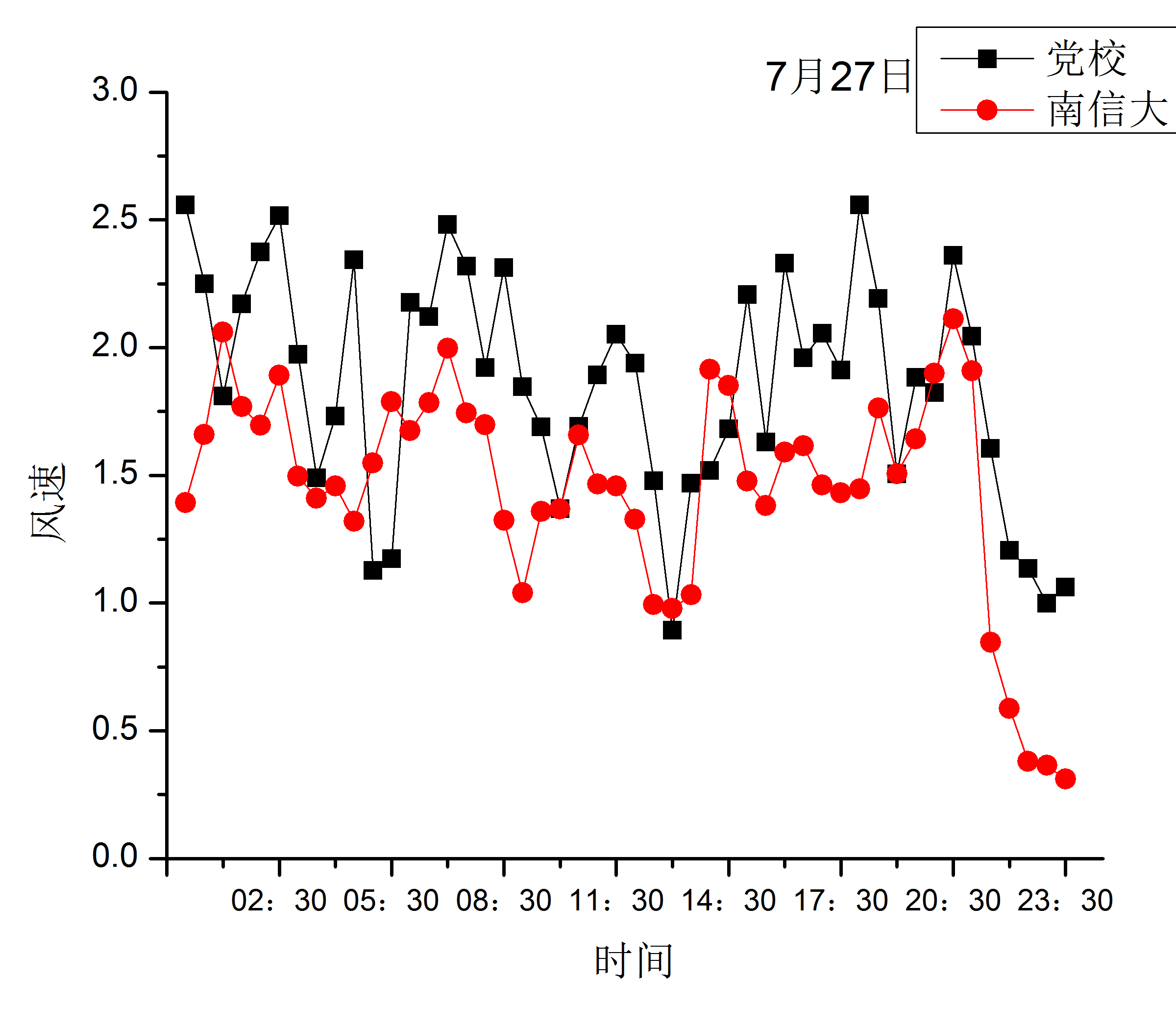
3.1.2 不同天气条件下的城郊平均风日变化对比 7
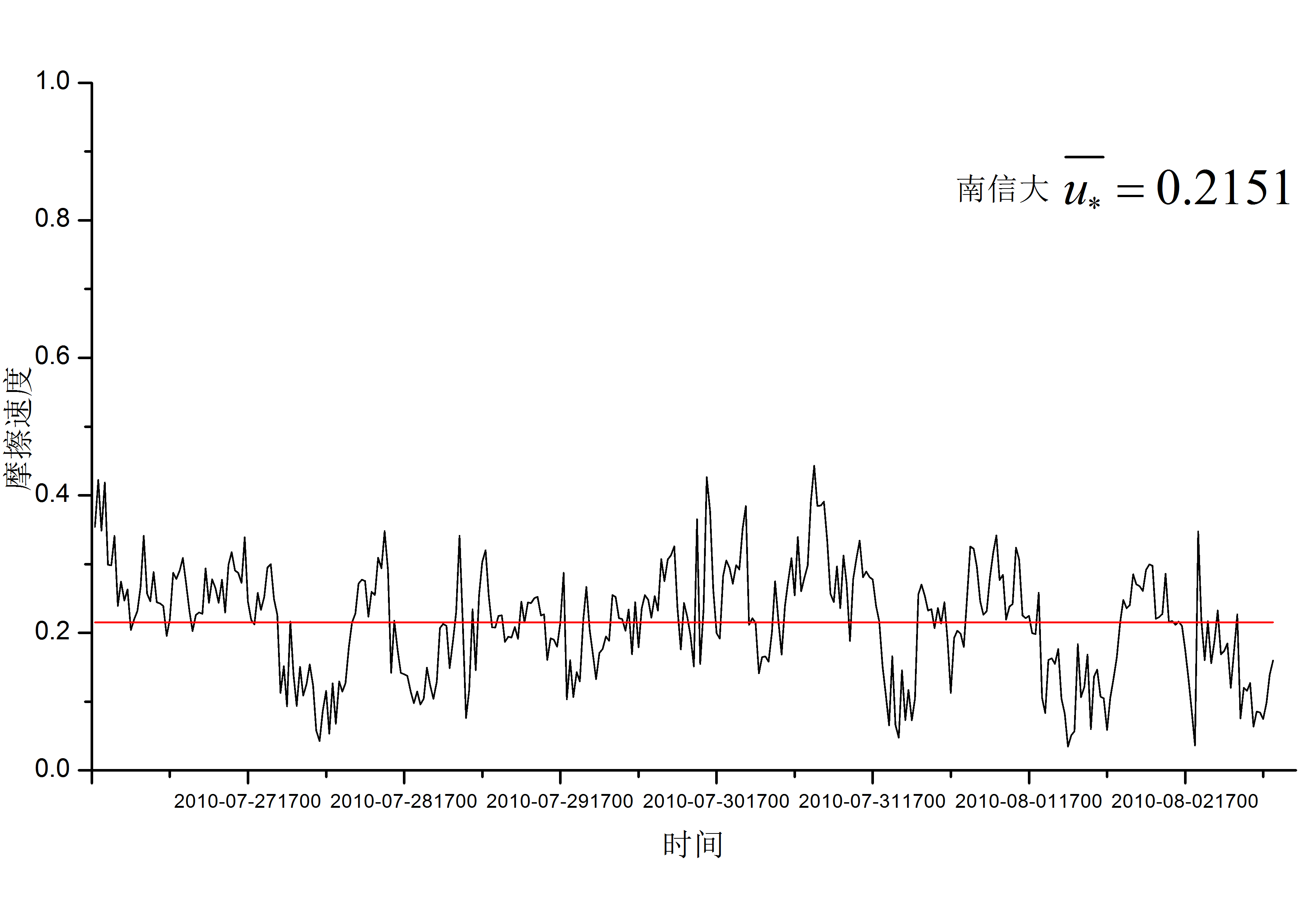
3.2 摩擦速度对比分析.....................................................8
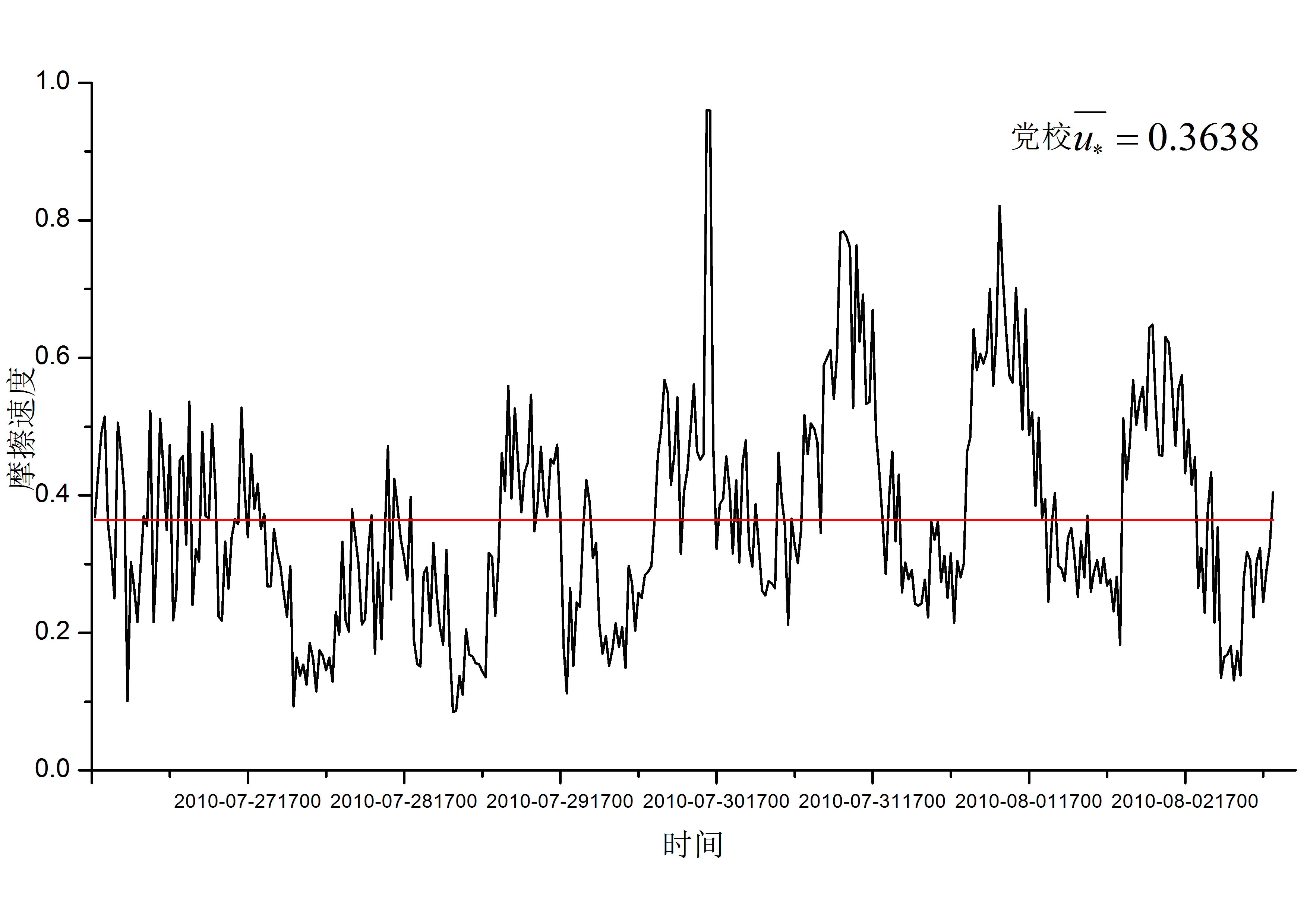
3.2.1总体变化趋势对比分析...........................................8
3.2.2不同天气条件下的城郊摩擦速度日变化对比.........................9
3.3 湍流强度分析........................................................10
3.3.1总体变化趋势对比分析..........................................10
3.3.2不同天气条件下的城郊湍流强度日变化对比.........................11
3.4 无量纲风速分量标准差随稳定度变化特征.................................12
3.4.1 水平归一化标准差..............................................12
3.4.2 垂直风速归一化标准差..........................................13
4 城、郊湍流通量对比研究................................14
4.1 观测期间城、郊湍流热通量的总体变化趋势............................14
4.2 不同天气条件下湍流热通量对比分析...................................15
5 总结 17
参考文献: 19
致谢 21
南京城郊下垫面湍流统计特性及湍流通量研究
胡艺膑
Abstract:In this paper, we use the 2010 July 26 to August 3 conducted Nanjing summer urban heat island experimental three-dimensional structure of turbulence observations, Statistics turbulence and turbulent fluxes NUIST PARTY observation field and two observation points were compared. The results show that: 1) the mean wind speed and the city and suburbs underlying surface friction velocity has diurnal variation characteristics to a certain extent, The average wind speed is greater than the urban city suburb Underlying Underlying, While daytime wind speed is greater than the whole night. The average rate of Urban surface friction of the underlying surface is greater than the suburbs. And during the day the whole is greater than the friction velocity night. 2) Urban surface turbulence intensity on the whole smaller than in the horizontal direction on the outskirts of the underlying surface, Urban surface and turbulence intensity was close to the suburbs.But the turbulence intensity in the vertical direction is significantly lower than the suburban city Underlying Underlying. 3) Normalized horizontal Urban surface wind speed is greater than the standard deviation Overall suburbs,Contrast city, suburban variation can be found on the outskirts of the data is more discrete, which is consistent with the strong turbulent suburbs greater volatility phase. 4) the outskirts of the underlying surface latent heat flux showed significant diurnal variation. At the same time latent heat flux almost always be greater than the sensible heat flux, suggesting that suburban summer turbulent energy mainly in the form of water vapor transport.In Urban surface latent heat flux is more discrete and not particularly obvious diurnal variation. At the same time, within the city turbulent heat flux sensible heat flux led, indicating that the city's water vapor transport is not obvious, this is a rare and cities for water evaporation Relations. Cloudy weather on the city, the suburbs of sensible heat flux influence is more obvious, while on the outskirts of the city on the underlying surface than the underlying surface.
Keyword: Urban and suburban comparison; turbulence statistic characteristics; turbulence heat fluxes
1 引言
1.1 研究目的
近年来随着城市化速度的加快,乡镇城市化和城市密集化的日益加深[1-6],城市环境问题比如城市热岛、城市污染等日益突出。在人口极度密集的城市环境中,城市工业污染物、车辆尾气及人们生活排放的大量污染物对人的身心健康、正常的生产生活构成严重威胁。因此研究污染物在城市下垫面的扩散和输送过程备变得极为重要[7-9]。城市污染物的扩散规律与大气湍流结构紧密相关[10-11]。通过对湍流结构特性和湍流通量的研究则可以发现湍流对动量、热量、湿度以及污染物等的输送。所以,对于城市下垫面大气湍流特征和湍流通量的研究能够加强对复杂下垫面大气结构的理解同时能够帮助解决城市环境问题。
1.2 国内外研究进展
1978年Oke[12]首次提出城市冠层( Urban Canopy Layer) 的概念,定义为从地面到建筑物屋顶,而从建筑物屋顶到积云中部的空气层则称为城市边界层( Urban Boundary Layer)。同其他下垫面相比较,城市下垫面显得更为复杂,这是由于城市化建设以及人类活动造成的热源排放,同时城市下垫面又和我们人类生活密切相关,因此对于城市复杂下垫面大气湍流特征和湍流通量的研究显得格外重要。
对城市下垫面大气湍流特征和湍流通量,国内外都有不同程度的研究。胡非等[13]对北京城市冠层大气湍流统计特征的研究结果表明城市冠层中湍流脉动强度和标准差几乎均大于平坦下垫面。刘辉志等[14]对北京城市下垫面边界层湍流统计特征的研究结果表明,在不稳定层结下,城市下垫面近地层无量纲速度方差随稳定度的变化关系基本上满足Monin-Obukhov 相似性理论。Roth[15]对50多个城市的湍流特征进行观测,给出了近地层无量纲速度方差与稳定度的变化关系。沈觉成等[16]的研究结果表明,湍流强度随大气稳定度的减少而增加,大气越不稳定,湍强就越强。何文等[17]和王新平等[18]的研究结果表明城市下垫面能量输送以感热为主,且感热通量的日变化受城市下垫面和人为热源影响。许丽人等[19]研究结果表明下垫面结构的差异明显地影响湍流量,且无量纲化标准差则表现出随下垫面粗糙度增加而减少的特征。
1.3 主要研究内容
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:15891字
相关图片展示: