论文总字数:43448字
摘 要
近年来,可见光通信(Visible Light Communication,VLC)技术已成为通信学术界和工业界关注的一大研究热点。该技术能够同时实现照明与无线通信功能,并且具有传输数据率高,保密性强,无需频谱认证,无电磁干扰等优点,其是未来无线通信系统中一项极具潜力的关键技术。
多输入多输出(Multiple-Input Multiple-Output,MIMO)技术和正交频分复用(Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing,OFDM)技术是现代射频无线通信系统中的两项核心传输技术。其中,MIMO技术在发射端和接收端配置多根天线,充分利用多维信道带来的空间自由度,在无需增加带宽和发射功率的前提下获得优于单输入单输出(Single-Input Single-Output,SISO)系统的信道容量;OFDM技术则将频域信道分成若干存在部分重叠的正交子信道,以并行方式在子信道上传输低速数据流,显著提高系统频谱利用率且有效抑制码间干扰。本文将考虑采用这两种技术提高可见光通信系统的性能,并重点关注接收端的检测算法设计。
首先,本文研究了非成像与成像两种MIMO可见光通信系统,并分别给出两种系统的信道矩阵计算方法,然后探索了接收机旋转对两种系统的影响,之后计算两种系统的信道矩阵,以对两种系统的特性进行比较。
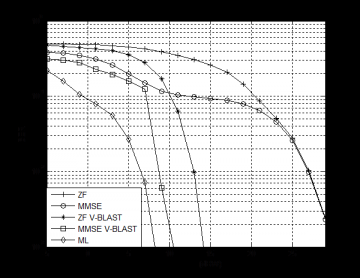
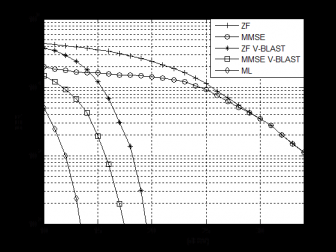
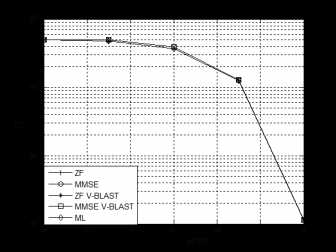
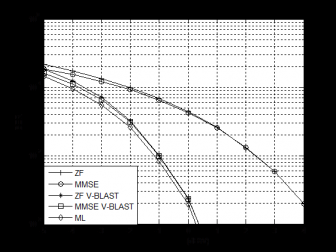
接着,本文介绍了五种经典MIMO检测算法:迫零(Zero Forcing,ZF)算法、最小均方误差(Minimum Mean Squared Error,MMSE)算法、最大似然(Maximum Likelihood,ML)算法、ZF垂直贝尔实验室分层空时(Vertical Bell Labs Layered Space-Time,V-BLAST)算法和MMSE V-BLAST算法并将它们应用到MIMO可见光通信系统中,之后通过蒙特卡洛仿真,比较各种MIMO检测算法的性能。
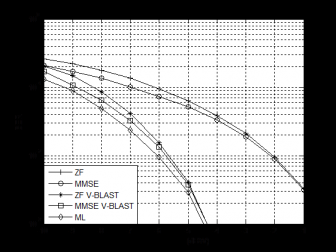
最后,本文描述了OFDM的基本原理以及OFDM在可见光通信中的两种修正形式:直流偏置光正交频分复用(DC-biased Optical OFDM,DCO-OFDM)与非对称修剪光正交频分复用(Asymmetrically-Clipped Optical OFDM,ACO-OFDM),然后将它们应用到MIMO可见光通信系统中,并提出了考虑削波噪声的改进MIMO检测算法,之后通过蒙特卡洛仿真对比ACO-OFDM与DCO-OFDM的功率利用率,并对各种MIMO检测算法及其改进形式的性能进行比较。
关键词:DCO-OFDM,ACO-OFDM,MIMO检测算法
ABSTRACT
In recent years, visible light communication (VLC) has become a research focus of academia and industry. It can provide lighting and wireless communication at the same time. Moreover, it also has advantages such as high data transmission rate, strong confidentiality, license free spectrum, immunity to electromagnetic interference, etc. Therefore, it has been acknowledged as a promising technology of future wireless communication system.
Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) are two core technologies of modern radio frequency communication systems. MIMO technology employs multiple transmitting antennas and multiple receiving antennas to take full advantage of spatial degrees of freedom provided by multidimensional channel. A MIMO system can achieve higher channel capacity than a single-input single-output (SISO) system without increasing bandwidth and power. OFDM technology divides the channel into several partially overlapping orthogonal sub-channels in frequency domain, and transmits low-rate data steams on these sub-channels concurrently. It dramatically improves spectrum efficiency and mitigates inter-symbol interference effectively. This paper will employ both technologies in visible light communication in order to enhance its performance, and focus on the design of detection algorithms at the receiver.
Firstly, we study non-imaging and imaging visible light communication systems, and show the computation methods of their channel matrices, respectively. Then we explore the effects of receiver rotation on both systems. After that we calculate the channel matrices of both systems so as to compare the characteristics of the two systems.
Secondly, we introduce five classic MIMO detection algorithms: zero forcing (ZF) algorithm, minimum mean square error (MMSE) algorithm, maximum likelihood (ML) algorithm, ZF vertical bell layered space-time (ZF V-BLAST) algorithm and MMSE V-BLAST algorithm. We apply them to MIMO visible light communication systems, and then compare the performance of these MIMO detection algorithms by Monte Carlo simulation.
Finally, we describe the basic principle of OFDM and two modified OFDM schemes in visible light communication: DC-biased optical OFDM (DCO-OFDM) and asymmetrically-clipped optical OFDM (ACO-OFDM). Then we apply the two modified OFDM schemes to MIMO visible light communication systems, and propose improved MIMO detection algorithms that take clipping noise into account. After that we use Monte Carlo simulation to compare the power efficiency of DCO-OFDM and ACO-OFDM, and performance of various MIMO detection algorithms and their improved forms.
Keywords: DCO-OFDM, ACO-OFDM, MIMO detection algorithm
符号说明
| 向量x或矩阵X的转置 |
| 向量x或矩阵X的共轭转置 |
| 圆周率 |
e | 自然常数 |
ec | 电子电荷 |
| 统计平均 |
| 矩阵X的逆 |
| 矩阵X的伪逆 |
| 标量x的绝对值 |
IN | N×N的单位矩阵 |
| 概率 |
| 符号判决 |
| 使得f (x)最小的x |
| 使得f (x)最大的x |
| 正比符号 |
| 向量x的2范数 |
| 循环卷积 |
| 向量或矩阵对应元素相乘 |
| 快速傅里叶变换 |
| 快速傅里叶逆变换 |
| 取共轭 |
| 误差函数 |
| 余补误差函数 |
| 取实数部分 |
| 矩阵X的第 |
英文缩略语表
ACO-OFDM | Asymmetrically-Clipped Optical Orthogonal Frequency |
Division Multiplexing | |
AWGN | Additive White Gaussian Noise |
BER | Bit Error Rate |
CSI | Channel State Information |
DCO-OFDM | DC-biased Optical Orthogonal Frequency Division |
Multiplexing | |
DF | Decision Feedback |
DPIM | Digital Pulse Interval Modulation |
DPPM | Differential Pulse Position Modulation |
FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
FOV | Field of View |
IFFT | Inverse Fast Fourier Transform |
IM/DD | Intensity Modulation/Direct Detection |
ISI | Inter Symbol Interference |
LED | Light Emitting Diode |
LOS | Line of Sight |
MAP | Maximum A Posteriori |
MIMO | Multiple-Input Multiple-Output |
ML | Maximum Likelihood |
MMSE | Minimum Mean Squared Error |
NLOS | Non Line Of Sight |
NRZ-OOK | Non-Return-to-Zero On-Off Keying |
OFDM | Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing |
OOK | On-Off Keying |
OSM | Optical Spatial Modulation |
PAPR | Peak to Average Power Ratio |
PAM | Pulse Amplitude Modulation |
PAM-DMT | Pulse Amplitude Modulation Discrete Multi-Tone |
PD | Photo Diode |
PPM | Pulse Position Modulation |
QAM | Quadrature Amplitude Modulation |
RDPIM | Reverse Digital Pulse Interval Modulation |
RDPPM | Reverse Differential Pulse Position Modulation |
ROOKRZ | Reverse On-Off Keying and Return to Zero |
RPPM | Reverse Pulse Position Modulation |
SCFDE | Single Carrier Frequency Domain Equalization |
SIMO | Single-Input Multiple-Output |
SINR | Signal to Interference and Noise Ratio |
SISO | Single-Input Single-Output |
SNR | Signal to Noise Ratio |
STBC | Space-Time Block Code |
V-BLAST | Vertical Bell Labs Layered Space-Time |
VLC | Visible Light Communication |
ZF | Zero Forcing |
目录
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 论文的研究背景 1
1.2 论文的研究工作 2
第二章 MIMO可见光通信系统模型 5
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:43448字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;

 ,
,
 ,
,

















 列
列
