论文总字数:31670字
摘 要
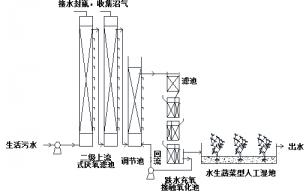
农村污染已经成为太湖流域面源污染的主要来源,我国农村分散式生活污水处理技术缺乏技术储备,输送到城镇污水处理厂管线太长,造价太高,所以需要设计一种便于农村使用,又不需要太高维修和运营成本的小型分散式农村生活污水生物生态组合工艺,将农村生活污水净化,保护水环境。论文开展了课题组构建开发了“厌氧产沼--缺氧反硝化及脱臭→跌水曝气好氧接触氧化→污染净化型农作物种植人工湿地”的生物生态组合工艺的研究,并开展了相关的工程设计。试验以无锡分校生活污水为处理对象,研究考察了本组合工艺处理生活污水的影响参数,确定了最佳运行参数,并得出以下结论:
(1)厌氧反应器在4种工况(水力停留时间HRT分别是24小时、48小时、72小时和96小时)下分别运行15天。结果表明,COD的去除率随着HRT的增大而上升,并且溶解性COD与HRT在稳态下存在一定的相关性ET=1-1.065/HRT0.1258。反应器的沼气产气量受温度条件影响很大,并呈现极显著的正相关性。研究期间,厌氧反应器未出现酸化现象。
(2)试验通过对4种工况(HRT=1h、2h、3h、4h)下跌水充氧接触氧化池对COD、氨氮的去除效果以及系统充氧效果的研究和综合比较,确定了最佳水力停留时间为2h,在此工况下,COD去除率为55.1%,氨氮去除率为27.5%,跌水曝气接好氧触氧化装置充氧效果良好。从沿程分布规律看,一阶跌水对COD去除贡献率最高,氨氮在各级跌水氧化池内的去除率普遍较低,第一级滤池充氧效果最好。
(3)水生蔬菜型人工湿地在不同水力负荷(0.18m3/m2d,0.21 m3/m2d,0.25m3/m2d)下运行出水的处理效率均较高。COD去除率在50%左右,出水平均浓度39.3mg/L;总氮去除率在52%以上,平均出水浓度7.9mg/L;氨氮平均去除率达74.21%,出水平均浓度3.2mg/L;投加石膏后总磷去除率达86.3%。出水平均浓度0.44mg/L。
(4)试验期间,组合工艺对COD,总氮,氨氮,总磷的平均去除率分别达到了86.2%,64.76%,78.5%,86.33%,平均出水浓度依次是39.3mg/L,7.9 mg/L,4.41mg/L,0.44mg/L,达到了《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB18918-2002)一级A标准。
研究表明,本工艺可以充分利用和发挥厌氧产沼气、缺氧脱臭、好氧处理和人工湿地氮磷去除技术的各自优势,各个单元功能明确,是一套适于小型分散式生活污水处理的高效而低能耗技术。
利用无锡分校开展的生物生态组合工艺研究成果,完成一项规模为30m3/d的实际工程初步设计研究。
关键词:分散式污水 大深径比厌氧滤池 跌水曝气接触氧化 污染净化型农作物人工湿地
ABSTRACT
Rural pollution has become a major source of nonpoint source pollution in Taihu Lake Basin and currently there is no effective treatment approach for rural decentralized sewage. Delivering to the municipal wastewater treatment plant is unrealistic as pipelines are too long to repair; Direct discharge will affect the water quality of Taihu Lake Basin; Constructing sewage treatment plants in rural areas are too costly. So it is necessary to design an easy for rural usage, and not require high maintenance and operating costs. Then we came up with the small-scale decentralized rural sewage combination of biological and ecological processes, rural sewage purification, with the function of ensuring water quality in Taihu Lake Basin from rural non-point source worse impact. Our team developed the "anaerobic biogas→ anoxic denitrification and deodorization→ falling water aeration aerobic contact oxidation→ Contaminant type crop wetland" a combination of biological and ecological processes. The domestic sewage of Wuxi campus is treated by this combined process to determine the optimum operating parameters, and we conclude that:
(1) Four conditions (the hydraulic retention time (HRT) is 24 hours, 48 hours, 72 hours and 96 hours respectively) are set for the anaerobic reactors which keep running for 15 days each. The results show that removal rate of COD increase with HRT and there is certain quantitative relation between soluble COD and HRT: ET=1-1.065/HRT0.1258. The temperature conditions have great effect on the biogas production of the reactor and they show extremely significant positive correlation. During the study period, maximum gas production appears in the middle of April. In addition, there is no acidification phenomenon during the period of running.
(2) By comparing the removal efficiency of COD and ammonia nitrogen, and the aeration effect of the waterfall aeration contact oxidation unit under 4 conditions (HRT=1h,2h,3h,4h ), 2h is optimal. In this condition, the removal rate of COD and ammonia nitrogen is 55.1% and 27.5%, and the aeration effect is good. From the longitudinal distribution law, first drop gets the highest contribution rate on the removal of COD, the removal efficiency of ammonia of various oxidation pool is generally low and the aeration effect of the first filter is the best.
(3) The pollutant removal efficiency of vegetated wetland under different hydraulic loading(0.18m3/m2d,0.21 m3/m2d,0.25m3/m2d)are high. The removal rate of COD is about 50% and the average concentration of COD in the effluent is 39.3mg/L. The removal rate of total nitrogen (TN) is above 52% and the average concentration of TN in the effluent is 7.9mg/L. The removal rate of ammonia nitrogen (N-NH4 ) is 74.21% and the average concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the effluent is 3.2mg/L. After adding gypsum, the removal rate of total phosphorus (TP) reaches 86.3% and the average concentrations of TP in the effluent is 0.44mg/L.
(4) During the stable running period, the average removal rate of COD, TN, N-NH4 and TP in turn is 86.2%, 64.8%, 78.5% and 86.33% with the average concentration of the effluent is 39.3mg/L, 8.77mg/L, 4.41mg/L and 0.44mg/L. All indicators reach the class A emission standard of “Urban Sewage Treatment Plant Pollutant Discharge Standard" (GB 18918-2002).
The research shows that this technology can make full use of the respective advantages of anaerobic biogas production, hypoxia modulates, aerobic treatment and nitrogen and phosphorus removal by constructed wetland. The function of each unit is clear, therefor, this is a set of efficient and low energy consumption technology which is suitable for small-scale decentralized sewage treatment.
Keywords: decentralized sewage, anaerobic filter with high ratio of height to diameter, waterfall aeration contact oxidation, pollution purified type vegetable constructed wetland
目 录
摘 要 I
第一章 绪论 5
1.1 研究背景 5
1.2 农村生活污水处理技术研究 6
1.3 课题的研究目的及意义 7
第二章 实验装置及研究内容 8
3.1实验原水水质 8
3.2 工艺流程与试验装置 8
3.3 研究内容 11
3.4 实验分析及测定方法 11
第三章 厌氧生物滤池工艺性能研究 12
4.1 COD处理效果研究 15
4.2 产气特性分析 17
4.3 VFA、pH和碱度的变化 19
4.4 氨氮的变化 19
4.5 本章小结 19
第四章 跌水充氧接触氧化池工艺性能研究 21
5.1 最佳水力停留时间的确定 21
5.2 各级接触氧化池的运行性能比较 23
5.3本章小结 25
第五章 人工湿地工艺性能研究 27
6.1 人工湿地对COD去除效果研究 27
6.2 人工湿地对氮的去除效果研究 27
6.3 人工湿地对磷的去除效果研究 29
6.4 本章小结 30
第六章 组合工艺总处理效果 32
7.1 组合工艺对COD的去除效果 32
7.2 组合工艺对氮的去除效果 32
7.3 组合工艺对总磷的去除效果 33
第七章 研究应用实例设计 34
8.1 设计任务及规模 34
8.2进出水水质 34
8.3设计依据 34
8.4工艺流程说明 34
8.5工艺参数 35
8.6构筑物设计 35
8.7工程细节说明 38
第八章 结论与建议 39
9.1主要结论 39
9.2主要建议 40
谢辞 41
参考文献 42
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景
1.1.1 太湖地区水污染现状
根据中国环境监测总站在2015年1 月的环境监测水质月报[1]:太湖主要环湖河流总体为轻度污染,主要污染指标为氨氮、总磷和高锰酸盐指数。监测的28条河流的34个断面的水质类别为:Ⅰ~Ⅲ类水质占35%,Ⅳ、Ⅴ类占47%,劣Ⅴ类占18%。与上月及去年同期相比,水质无明显变化。
2015年1月江苏省环境状况公报[2] 表明:92个集中式饮用水水源地水质全部达标。全省水环境质量总体保持稳定。国控断面水质符合Ⅲ类比例和太湖流域重点断面达标率同比上升,国控断面水质劣于Ⅴ类的断面比例有所增加;淮河流域考核断面和长江流域考核及评估断面达标率同比有所下降。
尽管太湖地区投入大量经费和人力、物力治理太湖污染,太湖地区水质的排放标准已经大幅度提高,大湖每年富营养化趋势仍然严重,没有好转的趋势。所以不仅需要着眼于城市生活、生产污水的治理,还需要放眼农业面源的污染。
1.1.2 治理太湖流域农村生活污水的必要性
从1987年至今,太湖水体富营养化问题日趋严重,太湖流域水污染防治势在必行。太湖流域水污染防治的主要战略思想是:控源截污、修复和重建基础生态环境、改善河湖水质,而其中,控源截污是太湖流域水污染防治的首要任务。目前量小、分散、面广的农村生活污水已成为加剧太湖富营养化进程的主要原因之一。富营养化治理的根本在于控制入湖的氮、磷营养负荷,而农村生活污水的排放对太湖氮、磷污染的贡献率分别达25. 1% ,60. 0%[3]。
1.2 农村生活污水处理技术研究
我国农村生活污水处理的历史较短,近十年以来国家才开始重视并大力支持发展农村生活污水的处理设施的研究,目前在我国实施的已经成型的工艺可分为三类,一类是利用仅为生态处理过程处理农村生活污水,第二类是将现有城市污水处理设施小型化并集成化,第三类是参考国内外的相关技术,结合国内农村生活污水处理现状进行自主研发的新型农村生活污水处理装置。前两类做法不能有效解决我国农村污水处理的难题,因而国家在十二五期间开展农村污水处理研发的重大专项课题,东南大学成为该课题的负责单位。
1.2.1 自然处理
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:31670字
相关图片展示:




该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


