论文总字数:22651字
目 录
1 绪论 5
1.1研究背景 5
1.2常用的除磷方法 6
1.2.1吸附法 6
1.2.2离子交换法 6
1.2.3膜分离法 7
1.2.4化学沉淀法 7
1.2.5生物法 8
1.3氧化锆在环保方面的运用 8
1.4生物炭的性质 8
1.4.1生物炭的元素构成 8
1.4.2生物炭的酸碱性 8
1.4.3生物炭的化学性质团及物理特性 9
1.4.4生物炭的稳定性 9
1.5本课题的内容与目的 9
1.5.1研究目的 9
1.5.2研究的内容 9
2 氧化锆改性芦苇生物炭的制备与实验方法 10
2.1 实验的材料与仪器 10
2.1.1实验所需的药剂与原材料 10
2.1.2实验所需的仪器 10
2.2 实验方法 11
2.2.1氧化锆改性芦苇生物炭的表征 11
2.2.2改性生物炭的制备 11
2.2.3绘制磷标准曲线 11
2.2.4不同酸碱条件下对吸附能力的影响 11
2.2.5不同Zr/C的投加比对吸附能力的影响 11
2.2.6不同的改性生物炭投加量对吸附能力的影响 11
2.2.7改性生物炭吸附不同浓度磷的动力学 12
2.2.8吸附等温线实验 12
2.2.9共存阴离子实验 12
3 实验结果及讨论 13
3.1 氧化锆改性芦苇生物炭的表征 13
3.2不同酸碱条件下对吸附能力的影响 13
3.3不同Zr/C的投加比对吸附能力的影响 14
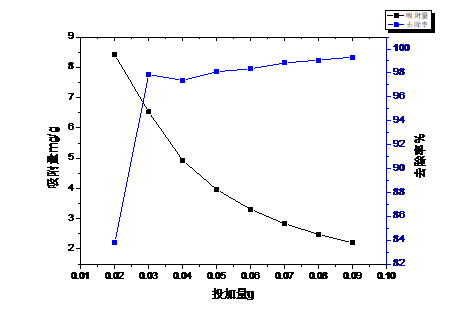
3.4不同的改性生物炭投加量对吸附能力的影响 14
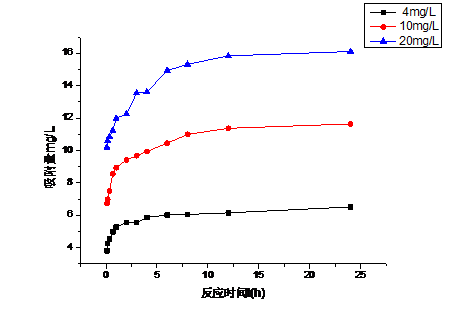
3.5 改性生物炭吸附不同浓度磷的动力学 15
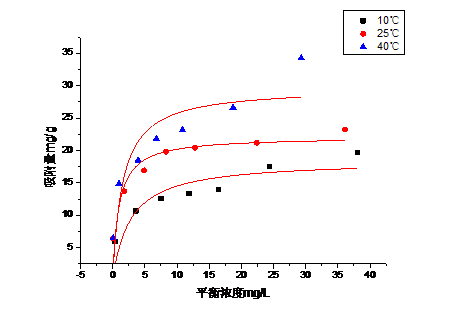
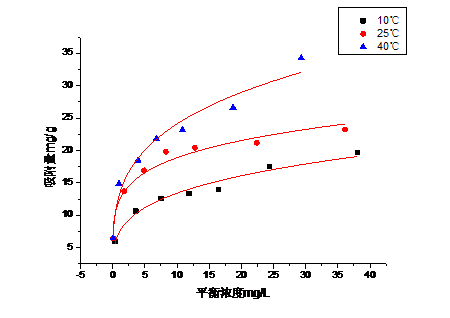
3.6 吸附等温线实验 16
3.7共存阴离子实验 17
4 结论 19
5 参考文献 20
致谢 22
锆改性芦苇生物炭去除废水中磷的研究
匡雨藤
,China
Abstract: This study has linked the two parts, because of the increasing pollution of phosphorus in natural and the fact that a large number of reed rods have been burned and destroyed. The experiment is the ordinary reed rod by pyrolysis of bio-charcoal, and then the use of zirconium oxychloride for modification. There are many experiments during this study to explore the properties and principles of adsorbent materials, such as p H, dosage, adsorption isotherm, kinetics and different C / Zr contents. The optimum conditions for the preparation of zirconium modified biochar and the removal of low concentration of phosphorus in water can be determined by the above experiments. In the case of pH 4 and the C / Zr ratio is 1/1, the best adsorption effect can be obtained. The removal rate of 0.03 g of modified biochar phosphorus in the phosphorus solution with the concentration of 4.0 mg / L can reach 97% , The adsorption capacity can reach 8.5mg / g. According to the formula of adsorption kinetics, the R2 of the first order equation is 0.812、0.97 and 0.993, and the R2 of the second order equation is 0.999、0.997 and 0.996. Therefore, the new material satisfies the false two levels, and the actual equilibrium adsorption capacity is 16.117mg / G = 0.98、0.97、0.97, and L-type 0.94、0.94、0.89、respectively, after the Langmiur and Frendlich equations were fitted at 10、25、 and 40 ℃, respectively, and the adsorption process was more in accordance with the Frendlich equation. We have also obtained that the process is dominated by chemical adsorption. After the coexisting ion experiments of Cl- 、CO32- and SO42-, we know that the influence of the three on the adsorbed phosphorus effect is small and the size of the effect is different. for SO42-gt; Cl-gt; CO32-. Through the experimental data show that the experiment obtained by the zirconium modified reed biochar on the water in the phosphorus has a good ability to remove.
Keywords:Biological activated carbon; adsorption; low concentration of phosphorus; zirconium modified;
1绪论
1.1 研究背景
水——地球的基础资源更是地球生命的宝贵财富尤其对于人类生存来说,它对于人类的生产、生活关系可以说是非常的密切。但是随着全球化经济的大趋势,以及城市、工业的急速发展很多城市的生活污水以及发展新区的工业废水被肆无忌惮的排放到自然环境中,因而导致了大面积的水体遭到严重的污染,尤其是生活污水中过量的磷酸盐和氨氮,导致水中水藻疯长[1]。水体富营养化所产生的连锁反应有水体腐臭从而会影响人类身体,造成巨大的自然资源浪费,甚至破坏周围的生态环境,比如之前的太湖事件。平原地区湖泊富营养化调查和评价[2]如表 1-1和1-2 所示:在进行检测营养状态的对象中,四分之一的湖泊状态处于中度富营养,大概有一半平原湖泊状态处于轻度营养化,只有太白湖因受到磷污染而状态处于重度富营养化,而如此现象我们只是在抽取了15个湖泊得到的结果。
表1-1 湖泊富营养化分级和判断标准
Table.1-1 Evaluation and grading standard of lake eutrophication
综合营养状态指数 | 营养状态 |
lt;30 | 贫营养 |
30-50 | 中营养 |
50-60 | 轻度富营养 |
60-70 | 中度富营养 |
gt;70 | 重富营养 |
表2-2 东部平原调查湖泊富营养化评价
Table.1-2 Evaluation of lake eutrophication in Eastern Plain
湖泊 | TLI ( ∑ ) | 营养水平 |
太白湖 | 77.49 | 重度营养 |
太湖 | 62.86 | 中度富营养 |
巢湖 | 61.98 | 中度富营养 |
鄱阳湖 | 61.34 | 中度富营养 |
东平湖 | 60.11 | 中度富营养 |
梁子湖 | 59.15 | 轻度富营养 |
衡水湖 | 56.98 | 轻度富营养 |
固城湖 | 56.49 | 轻度富营养 |
微山湖 | 55.17 | 轻度富营养 |
南漪湖 | 54.85 | 轻度富营养 |
洪泽湖 | 54.06 | 轻度富营养 |
升金湖 | 53.16 | 轻度富营养 |
龙感湖 | 51.97 | 轻度富营养 |
石臼湖 | 47.43 | 中营养 |
骆马湖 | 41.87 | 中营养 |
造成水体富营养化的主要因素之一就是磷酸盐[3],因为城市的逐渐发展和人们的生活水平的提升,大量的含磷酸盐和氨氮的工业废盐水和生活污水没有严格达标就排入到自然水体中,从侧面促使了水体富营养化。关于水体的富营养化意思是在社会生产活动中,未能经过处理就排至自然水体中的磷酸根超标废水,超过了水体所能调节的范围,使得水体中动植物的无节制的繁衍,造成水中的溶解氧被过度损耗,水生动物缺氧死亡导致水体水质恶化发臭,大规模的破坏水体的生态环境的平衡的现象。如果产生了水体的富营养化,最先造成的结果就是水体各项指标的超标及水质恶化[4-6],浮游生物、水藻等水生动植物过度的繁殖,水体变得浑浊不清,如果后期水体的营养物质被消耗殆尽藻类生物就会因缺少必要的营养物质而死亡,这个因素会直接导致水体产生臭味。当自然水体的水质受到如此之大的影响时,接着就会对自来水厂的净化过程产生极大的挑战,直接会影响到出水的水质[7,8],例如过度繁殖的藻类或是其他浮游生物会对水库的进出水系统和设备造成堵塞的威胁,降低供水处的过滤效率、严重影响水质的出水指标。不光如此,水体富营养化还会降低水产养殖业的收入[9,10],最简单的解释就是,由于水体中疯长的藻类,过度消耗了水体中的溶解氧,直接导致水生动物鱼、虾等生物的死亡,使得养殖业遭受严重的损失,同时水生动物缺氧而死后在水中腐败又会氨氮、磷的排放造成恶性循环。由此看出,迫在眉睫的问题就是采用某种高效的方法除去水体中的磷酸盐,而这也正是修复水环境的关键。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:22651字
相关图片展示:

该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


